Hemopexin dosing improves cardiopulmonary dysfunction in murine sickle cell disease
- PMID: 34478834
- PMCID: PMC9231663
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.08.238
Hemopexin dosing improves cardiopulmonary dysfunction in murine sickle cell disease
Abstract
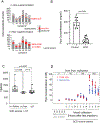
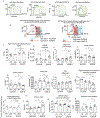
Hemopexin (Hpx) is a crucial defense protein against heme liberated from degraded hemoglobin during hemolysis. High heme stress creates an imbalance in Hpx bioavailability, favoring heme accumulation and downstream pathophysiological responses leading to cardiopulmonary disease progression in sickle cell disease (SCD) patients. Here, we evaluated a model of murine SCD, which was designed to accelerate red blood cell sickling, pulmonary hypertension, right ventricular dysfunction, and exercise intolerance by exposure of the mice to moderate hypobaric hypoxia. The sequence of pathophysiology in this model tracks with circulatory heme accumulation, lipid oxidation, extensive remodeling of the pulmonary vasculature, and fibrosis. We hypothesized that Hpx replacement for an extended period would improve exercise tolerance measured by critical speed as a clinically meaningful therapeutic endpoint. Further, we sought to define the effects of Hpx on upstream cardiopulmonary function, histopathology, and tissue oxidation. Our data shows that tri-weekly administrations of Hpx for three months dose-dependently reduced heme exposure and pulmonary hypertension while improving cardiac pressure-volume relationships and exercise tolerance. Furthermore, Hpx administration dose-dependently attenuated pulmonary fibrosis and oxidative modifications in the lung and myocardium of the right ventricle. Observations in our SCD murine model are consistent with pulmonary vascular and right ventricular pathology at autopsy in SCD patients having suffered from severe pulmonary hypertension, right ventricular dysfunction, and sudden cardiac death. This study provides a translational evaluation supported by a rigorous outcome analysis demonstrating therapeutic proof-of-concept for Hpx replacement in SCD.
Keywords: Critical speed; Exercise tolerance; Pulmonary vascular disease; Right ventricular function.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Targeting lung heme iron by aerosol hemopexin adminstration in sickle cell disease pulmonary hypertension.Free Radic Biol Med. 2025 Mar 1;229:458-473. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2025.01.045. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Free Radic Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 39862998
-
Depletion of haptoglobin and hemopexin promote hemoglobin-mediated lipoprotein oxidation in sickle cell disease.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018 Nov 1;315(5):L765-L774. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00269.2018. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30047285 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic Overexpression of Hemopexin Inhibits Inflammation and Vascular Stasis in Murine Models of Sickle Cell Disease.Mol Med. 2016 Sep;22:437-451. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2016.00063. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27451971 Free PMC article.
-
Double-edged functions of hemopexin in hematological related diseases: from basic mechanisms to clinical application.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 1;14:1274333. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1274333. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hemopexin and haptoglobin: allies against heme toxicity from hemoglobin not contenders.Front Physiol. 2015 Jun 30;6:187. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2015.00187. eCollection 2015. Front Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26175690 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Moderate hypoxia induces metabolic divergence in circulating monocytes and tissue resident macrophages from Berkeley sickle cell anemia mice.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 12;10:1149005. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1149005. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37502360 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting heme in sickle cell disease: new perspectives on priapism treatment.Front Physiol. 2024 Jul 17;15:1435220. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1435220. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39086934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting lung heme iron by aerosol hemopexin adminstration in sickle cell disease pulmonary hypertension.Free Radic Biol Med. 2025 Mar 1;229:458-473. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2025.01.045. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Free Radic Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 39862998
-
The Role of Inflammation in The Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Cardiopulmonary Complications of Sickle Cell Disease.Biomolecules. 2023 Feb 17;13(2):381. doi: 10.3390/biom13020381. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36830749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular consequences of sickle cell disease.Biophys Rev (Melville). 2022 Aug 8;3(3):031302. doi: 10.1063/5.0094650. eCollection 2022 Sep. Biophys Rev (Melville). 2022. PMID: 38505276 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McCavit TL. Sickle cell disease. Pediatr Rev. 2012;33(5):195–204; quiz 5-6. - PubMed
-
- Simpson S Sickle cell disease: a new era. Lancet Haematol. 2019;6(8):e393–e4. - PubMed
-
- E MJ, and T TA. Sickle Cell Anemia. Medscape. 2020.
-
- Fushimi N, Sawada H, Udaka F, and Kameyama M. [Five-year follow-up studies of laboratory data in the elderly group]. Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi. 1989;26(2):179–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

