Vascular e-Learning During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The EL-COVID Survey
- PMID: 34478845
- PMCID: PMC8407942
- DOI: 10.1016/j.avsg.2021.08.001
Vascular e-Learning During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The EL-COVID Survey
Abstract
Background: The corona virus disease (COVID-19) pandemic has radically changed the possibilities for vascular surgeons and trainees to exchange knowledge and experience. The aim of the present survey is to inventorize the e-learning needs of vascular surgeons and trainees as well as the strengths and weaknesses of vascular e-Learning.
Methods: An online survey consisting of 18 questions was created in English, with a separate bilingual English-Mandarin version. The survey was dispersed to vascular surgeons and trainees worldwide through social media and via direct messaging from June 15, 2020 to October 15, 2020.
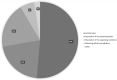
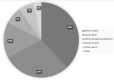
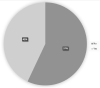
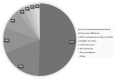
Results: Eight hundred and fifty-six records from 84 different countries could be included. Most participants attended several online activities (>4: n = 461, 54%; 2-4: n = 300, 35%; 1: n = 95, 11%) and evaluated online activities as positive or very positive (84.7%). In deciding upon participation, the topic of the activity was most important (n = 440, 51.4%), followed by the reputation of the presenter or the panel (n = 178, 20.8%), but not necessarily receiving accreditation or certification (n = 52, 6.1%). The survey identified several shortcomings in vascular e-Learning during the pandemic: limited possibility to attend due to lack of time and increased workload (n = 432, 50.5%), no protected/allocated time (n = 488, 57%) and no accreditation or certification, while technical shortcomings were only a minor problem (n = 25, 2.9%).
Conclusions: During the COVID-19 pandemic vascular e-Learning has been used frequently and was appreciated by vascular professionals from around the globe. The survey identified strengths and weaknesses in current e-Learning that can be used to further improve online learning in vascular surgery.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Zymvragoudakis V, Matheiken S, Patelis N. Analysis of the Greek vascular surgical trainees’ appreciation of e-learning. Hellenic J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019;1:130–135.
-
- Matheiken SJ, Verstegen D, Beard J, et al. E-learning resources for vascular surgeons: a needs analysis study. J Surg Educ. 2012;69:477–482. - PubMed
-
- Maertens H, Madani A, Landry T, et al. Systematic review of e-learning for surgical training. Br J Surg. 2016;103:1428–1437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical