Clinical feature of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS)-associated encephalitis/encephalopathy: a retrospective study
- PMID: 34479504
- PMCID: PMC8418043
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-021-06627-1
Clinical feature of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS)-associated encephalitis/encephalopathy: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background/objective: Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) cause encephalitis/encephalopathy, but few reports were available. We aimed to investigate the incidence of encephalitis/encephalopathy in SFTS patients and to summarize clinical characteristics, laboratory findings and imaging features.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of all patients with confirmed SFTS admitted to Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, a tertiary hospital in Nanjing City, China, between January 2016 and July 2020. The patients were divided into two groups according to whether they had encephalitis/encephalopathy: encephalitis/encephalopathy group and non- encephalitis/encephalopathy group. Clinical data, laboratory findings, imaging characteristics, treatments and outcomes of these patients were collected and analyzed.
Results: A total of 109 SFTS patients with were included, of whom 30 (27.5 %) developed encephalitis/encephalopathy. In-hospital mortality (43.3 %) was higher in encephalitis/encephalopathy group than non-encephalitis/encephalopathy group (12.7 %). Univariate logistic regression showed that cough, wheezing, dyspnoea, respiratory failure, vasopressors use, bacteremia, invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA) diagnoses, PCT > 0.5 ug/L, CRP > 8 mg/L, AST > 200 U/L and serum amylase level > 80 U/L were the risk factors for the development of encephalitis/encephalopathy for SFTS patients. Multivariate logistic regression analysis identified bacteremia, PCT > 0.5 mg/L and serum amylase level > 80 U/L as independent predictors of encephalitis/ encephalopathy development for SFTS patients.
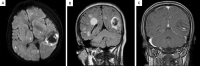
Conclusions: SFTS-associated encephalitis/encephalopathy has high morbidity and mortality. it was necessary to strengthen the screening of CSF testing and brain imaging after admission for SFTS patients who had symptoms of encephalitis/encephalopathy. SFTS patients with bacteremia, PCT > 0.5 ug/L or serum amylase level > 80 U/L should be warned to progress to encephalopathy.
Keywords: Amylase; Bacteremia; Cerebrospinal fluid; Encephalitis; Encephalopathy; Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome; Vasopressor.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

