RNA sequencing of blood in coronary artery disease: involvement of regulatory T cell imbalance
- PMID: 34479557
- PMCID: PMC8414682
- DOI: 10.1186/s12920-021-01062-2
RNA sequencing of blood in coronary artery disease: involvement of regulatory T cell imbalance
Abstract
Background: Cardiovascular disease had a global prevalence of 523 million cases and 18.6 million deaths in 2019. The current standard for diagnosing coronary artery disease (CAD) is coronary angiography. Surprisingly, despite well-established clinical indications, up to 40% of the one million invasive cardiac catheterizations return a result of 'no blockage'. The present studies employed RNA sequencing of whole blood to identify an RNA signature in patients with angiographically confirmed CAD.
Methods: Whole blood RNA was depleted of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and analyzed by single-molecule sequencing of RNA (RNAseq) to identify transcripts associated with CAD (TRACs) in a discovery group of 96 patients presenting for elective coronary catheterization. The resulting transcript counts were compared between groups to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs).
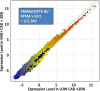
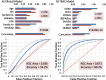
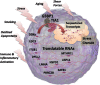
Results: Surprisingly, 98% of DEGs/TRACs were down-regulated ~ 1.7-fold in patients with mild to severe CAD (> 20% stenosis). The TRACs were independent of comorbid risk factors for CAD, such as sex, hypertension, and smoking. Bioinformatic analysis identified an enrichment in transcripts such as FoxP1, ICOSLG, IKZF4/Eos, SMYD3, TRIM28, and TCF3/E2A that are likely markers of regulatory T cells (Treg), consistent with known reductions in Tregs in CAD. A validation cohort of 80 patients confirmed the overall pattern (92% down-regulation) and supported many of the Treg-related changes. TRACs were enriched for transcripts associated with stress granules, which sequester RNAs, and ciliary and synaptic transcripts, possibly consistent with changes in the immune synapse of developing T cells.
Conclusions: These studies identify a novel mRNA signature of a Treg-like defect in CAD patients and provides a blueprint for a diagnostic test for CAD. The pattern of changes is consistent with stress-related changes in the maturation of T and Treg cells, possibly due to changes in the immune synapse.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Biomarker; Cilia; Coronary artery disease; FoxP1; FoxP3; Immune synapse; RNA sequencing; Regulatory T cells; Stress granules; Transcriptome; Treg.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
TM, TJ, and IT have an equity interest in True Bearing Diagnostics, Inc., a diagnostics company developing RNA biomarkers for various diseases, including coronary artery disease. IT, GSL3, RK, and TM are seeking patent protection for a commercial diagnostic test, without restriction for research uses.
Figures





References
-
- Kohn MA, Kwan E, Gupta M, Tabas JA. Prevalence of acute myocardial infarction and other serious diagnoses in patients presenting to an urban emergency department with chest pain. J Emerg Med. 2005;29(4):383–390. - PubMed
-
- Klinkman MS, Stevens D, Gorenflo DW. Episodes of care for chest pain: a preliminary report from MIRNET. Michigan Research Network. J Fam Pract. 1994;38(4):345–352. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

