Oncogenic HSP90 Facilitates Metabolic Alterations in Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas
- PMID: 34479963
- PMCID: PMC8530929
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-2734
Oncogenic HSP90 Facilitates Metabolic Alterations in Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas
Abstract
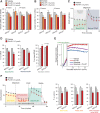
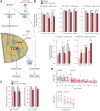
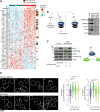
HSP90 is critical for maintenance of the cellular proteostasis. In cancer cells, HSP90 also becomes a nucleating site for the stabilization of multiprotein complexes including signaling pathways and transcription complexes. Here we described the role of this HSP90 form, referred to as oncogenic HSP90, in the regulation of cytosolic metabolic pathways in proliferating B-cell lymphoma cells. Oncogenic HSP90 assisted in the organization of metabolic enzymes into non-membrane-bound functional compartments. Under experimental conditions that conserved cellular proteostasis, oncogenic HSP90 coordinated and sustained multiple metabolic pathways required for energy production and maintenance of cellular biomass as well as for secretion of extracellular metabolites. Conversely, inhibition of oncogenic HSP90, in absence of apparent client protein degradation, decreased the efficiency of MYC-driven metabolic reprogramming. This study reveals that oncogenic HSP90 supports metabolism in B-cell lymphoma cells and patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, providing a novel mechanism of activity for HSP90 inhibitors. SIGNIFICANCE: The oncogenic form of HSP90 organizes and maintains functional multienzymatic metabolic hubs in cancer cells, suggesting the potential of repurposing oncogenic HSP90 selective inhibitors to disrupt metabolism in lymphoma cells.
©2021 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures



References
-
- Calvo-Vidal MN, Cerchietti L. The metabolism of lymphomas. Curr Opin Hematol 2013;20:345–54. - PubMed
-
- Vajpayee N, Thakral C, Gopaluni S, Newman N, Gajra A. Activation of mammalian target of rapamycin in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a clinicopathological study. Leuk Res 2012;36:1403–9. - PubMed
-
- Dang CV, Lewis BC. Role of oncogenic transcription factor c-Myc in cell cycle regulation, apoptosis and metabolism. J Biomed Sci 1997;4:269–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

