Early treatment of COVID-19 with anakinra guided by soluble urokinase plasminogen receptor plasma levels: a double-blind, randomized controlled phase 3 trial
- PMID: 34480127
- PMCID: PMC8516650
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-021-01499-z
Early treatment of COVID-19 with anakinra guided by soluble urokinase plasminogen receptor plasma levels: a double-blind, randomized controlled phase 3 trial
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Early treatment of COVID-19 with anakinra guided by soluble urokinase plasminogen receptor plasma levels: a double-blind, randomized controlled phase 3 trial.Nat Med. 2021 Oct;27(10):1850. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01569-2. Nat Med. 2021. PMID: 34625750 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
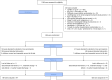
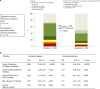
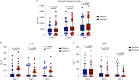
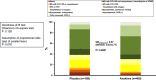
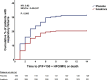
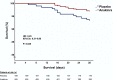
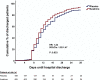
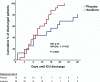
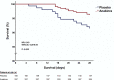
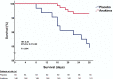
Early increase of soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) serum levels is indicative of increased risk of progression of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) to respiratory failure. The SAVE-MORE double-blind, randomized controlled trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of anakinra, an IL-1α/β inhibitor, in 594 patients with COVID-19 at risk of progressing to respiratory failure as identified by plasma suPAR ≥6 ng ml-1, 85.9% (n = 510) of whom were receiving dexamethasone. At day 28, the adjusted proportional odds of having a worse clinical status (assessed by the 11-point World Health Organization Clinical Progression Scale (WHO-CPS)) with anakinra, as compared to placebo, was 0.36 (95% confidence interval 0.26-0.50). The median WHO-CPS decrease on day 28 from baseline in the placebo and anakinra groups was 3 and 4 points, respectively (odds ratio (OR) = 0.40, P < 0.0001); the respective median decrease of Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score on day 7 from baseline was 0 and 1 points (OR = 0.63, P = 0.004). Twenty-eight-day mortality decreased (hazard ratio = 0.45, P = 0.045), and hospital stay was shorter.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
G.P. has received independent educational grants from Pfizer, MSD, Angelini and Bio-Rad. H.M. reports receiving honoraria, consulting fees and non-financial support from healthcare companies, including Amgen, Angelini, Bayer, Mylan, MSD, Pfizer and Servier. L.D. received consultation honoraria from Sobi. M.B. has received funds for research grants and/or advisor/consultant and/or speaker/chairman from Angelini, Astellas, Bayer, bioMérieux, Cidara, Cipla, Gilead, Menarini, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Shionogi and Nabriva. M.G.N. is supported by an ERC Advanced Grant (no. 833247) and a Spinoza grant of the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research. He has also received independent educational grants from TTxD, GSK and ViiV Healthcare. J.E.-O. is a co-founder, shareholder and CSO of ViroGates, Denmark, and is a named inventor on patients on suPAR owned by Copenhagen University Hospital Hvidovre, Denmark. P.P. has received honoraria from Gilead, Janssen and MSD. G.N.D. is an advisor or lecturer for Ipsen, Pfizer, Genkyotex, Novartis and Sobi, has received research grants from Abbvie and Gilead and has served as principal investigator in studies for Abbvie, Novartis, Gilead, Novo Nordisk, Genkyotex, Regulus Therapeutics, Tiziana Life Sciences, Bayer, Astellas, Pfizer, Amyndas Pharmaceuticals, CymaBay Therapeutics, Sobi and Intercept Pharmaceuticals. E.J.G.-B. has received honoraria from Abbott, bioMérieux, Brahms, GSK, InflaRx, Sobi and XBiotech; independent educational grants from Abbott, AxisShield, bioMérieux, InflaRx, Johnson & Johnson, MSD, Sobi and XBiotech; and funding from the Horizon 2020 Marie-Curie Project European Sepsis Academy (granted to the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens) and the Horizon 2020 European Grants ImmunoSep and RISKinCOVID (granted to the Hellenic Institute for the Study of Sepsis). The other authors do not have any competing interests to declare.
Figures
Comment in
-
Calming the cytokine storm in COVID-19.Nat Med. 2021 Oct;27(10):1674-1675. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01500-9. Nat Med. 2021. PMID: 34480126 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

