Diagnostic yield of genetic testing in 324 infants with hypotonia
- PMID: 34480364
- PMCID: PMC9291145
- DOI: 10.1111/cge.14057
Diagnostic yield of genetic testing in 324 infants with hypotonia
Abstract
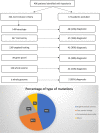
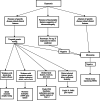
This retrospective cohort study was designed to determine the yield of genetic tests in hypotonic infants and develop a diagnostic algorithm. Out of 496 patients identified by International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 9/10 coding, 324 patients met the inclusion criteria. Diagnostic yields were 32% for karyotype, 19% for microarray, 30% for targeted genetic tests, 38% for gene panels, and 31% for exome sequencing. In addition, we considered the diagnostic contribution of ancillary tests, including neuroimaging, metabolic tests, and so forth. The combination of microarray and exome sequencing gave the highest diagnostic yield. None of the other tests added significant value in arriving at a diagnosis. Based on these results we propose that the vast majority of infants with congenital hypotonia should start with a microarray and proceed with exome sequencing, with the notable exception of infants with clearly syndromic features in whom karyotyping or targeted testing may be more appropriate.
Keywords: genetic testing; hypotonia; syndrome; whole exome sequencing.
© 2021 The Authors. Clinical Genetics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sparks SE. Neonatal hypotonia. Clin Perinatol. 2015;42(2):363‐371. - PubMed
-
- Le Pichon JB, Shapiro S. Neonatal Hypotonia. In: Stevenson DK, Cohen RS, Sunshine P, eds. Neonatology: Clinical Practice and Procedures. McGraw‐Hill Education; 2015:211‐235.
-
- Bodensteiner JB. The evaluation of the hypotonic infant. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 2008;15:10‐20. - PubMed
-
- Lisi EC, Cohn RD. Genetic evaluation of the pediatric patient with hypotonia: perspective from a hypotonia specialty clinic and review of the literature. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2011;53(7):586‐599. - PubMed
-
- Laugel V, Cossée M, Matis J, et al. Diagnostic approach to neonatal hypotonia: retrospective study on 144 neonates. Eur J Pediatr. 2008;167(5):517‐523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

