Recent technical advances in the study of nucleic acid modifications
- PMID: 34480848
- PMCID: PMC9109655
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.07.036
Recent technical advances in the study of nucleic acid modifications
Abstract
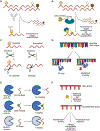
Enzyme-mediated chemical modifications of nucleic acids are indispensable regulators of gene expression. Our understanding of the biochemistry and biological significance of these modifications has largely been driven by an ever-evolving landscape of technologies that enable accurate detection, mapping, and manipulation of these marks. Here we provide a summary of recent technical advances in the study of nucleic acid modifications with a focus on techniques that allow accurate detection and mapping of these modifications. For each modification discussed (N6-methyladenosine, 5-methylcytidine, inosine, pseudouridine, and N4-acetylcytidine), we begin by introducing the "gold standard" technique for its mapping and detection, followed by a discussion of techniques developed to address any shortcomings of the gold standard. By highlighting the commonalities and differences of these techniques, we hope to provide a perspective on the current state of the field and to lay out a guideline for development of future technologies.
Keywords: 5-methylcytidine; DNA modification; N(4)-acetylcytidine; N(6)-methyladenosine; RNA modification; inosine; pseudouridine.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
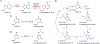


References
-
- Akichika S, Hirano S, Shichino Y, Suzuki T, Nishimasu H, Ishitani R, Sugita A, Hirose Y, Iwasaki S, Nureki O, and Suzuki T (2019). Cap-specific terminal N 6-methylation of RNA by an RNA polymerase II-associated methyltransferase. Science 363, eaav0080. - PubMed
-
- Bachellerie JP, Cavaillé J, and Hüttenhofer A (2002). The expanding snoRNA world. Biochimie 84, 775–790. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

