Higher Levels of C-Reactive Protein and Ferritin in Patients with Overweight and Obesity and SARS-CoV-2-Related Pneumonia
- PMID: 34482305
- PMCID: PMC8450829
- DOI: 10.1159/000517851
Higher Levels of C-Reactive Protein and Ferritin in Patients with Overweight and Obesity and SARS-CoV-2-Related Pneumonia
Abstract
Introduction: Overweight and obesity are associated with a more severe COronaVirus Disease 19 (COVID-19). Adipose tissue-related chronic inflammation could be a promoter for the occurrence of the cytokine storm that predicts aggravation of COVID-19. The primary aim was to investigate if this increased risk for more severe COVID-19 was associated with a higher inflammatory response.
Methods: We enrolled patients <75 years old hospitalized in a medical COVID-19 ward with SARS-CoV-2-related pneumonia. Patients were classified according to BMI as normal weight, overweight, and obesity. Laboratory parameters were measured at admission and every second day during the hospital stay.
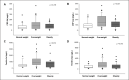
Results: Ninety patients (64.4% males; median age 61 years) were enrolled. Invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) was needed in 9% of the patients with normal weight, in 32.4% of the patients with overweight, and in 12.9% of the patients with obesity (p = 0.045). Maximal C-reactive protein (CRP) level during hospital stay was 92 (48-122) mg/L in patients with normal weight, 140 (82-265) mg/L in patients with overweight, and 117 (67-160) mg/L in patients with obesity (p = 0.037). Maximal ferritin values were 564 (403-1,379) μg/L in patients with a normal weight, 1,253 (754-2,532) μg/L in patients with overweight, and 828 (279-1,582) μg/L in patients with obesity (p = 0.015).
Conclusion: Patients with overweight and obesity required more IMV and had higher peaks of CRP and ferritin than patients with normal weight during COVID-19.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; Corona virus disease 19; Obesity; Overweight; Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus.
© 2021 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Goossens GH, Dicker D, Farpour-Lambert NJ, Frühbeck G, Mullerova D, Woodward E, et al. Obesity and COVID-19: a perspective from the European Association for the Study of obesity on immunological perturbations, therapeutic challenges, and opportunities in obesity. Obes Facts. 2020;13((4)):439–52. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

