Nuclear RNA Regulation by XRN2 and XTBD Family Proteins
- PMID: 34483148
- PMCID: PMC10511037
- DOI: 10.1247/csf.21041
Nuclear RNA Regulation by XRN2 and XTBD Family Proteins
Abstract
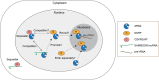
XRN2 is a 5'-to-3' exoribonuclease that is predominantly localized in the nucleus. By degrading or trimming various classes of RNA, XRN2 contributes to essential processes in gene expression such as transcription termination and ribosome biogenesis. Despite limited substrate specificity in vitro, XRN2 targets a specific subset of RNA by interacting with other proteins in cells. Here we review the functions of proteins that have an evolutionarily conserved XRN2-binding domain, XTBD. These proteins modulate activity of XRN2 by stabilizing it, controlling its subcellular localization or recruiting it to specific RNA targets, and thereby impact on various cellular processes.Key words: RNA regulation, XRN2, XTBD, ribosome biogenesis, subcellular localization.
Keywords: RNA regulation; XRN2; XTBD; ribosome biogenesis; subcellular localization.
Figures

References
-
- Amberg, D.C., Goldstein, A.L., and Cole, C.N.. 1992. Isolation and characterization of RAT1: an essential gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae required for the efficient nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of mRNA. Genes Dev., 6: 1173–1189. - PubMed
-
- Brannan, K., Kim, H., Erickson, B., Glover-Cutter, K., Kim, S., Fong, N., Kiemele, L., Hansen, K., Davis, R., Lykke-Andersen, J., and Bentley, D.L.. 2012. mRNA decapping factors and the exonuclease Xrn2 function in widespread premature termination of RNA polymerase II transcription. Mol. Cell, 46: 311–324. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chatterjee, S. and Grosshans, H.. 2009. Active turnover modulates mature microRNA activity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature, 461: 546–549. - PubMed

