Neurotransmitter Precursor Amino Acid Ratios Show Differential, Inverse Correlations with Depression Severity in the Low and High Depression Score Range
- PMID: 34483668
- PMCID: PMC8414612
- DOI: 10.1177/11786469211039220
Neurotransmitter Precursor Amino Acid Ratios Show Differential, Inverse Correlations with Depression Severity in the Low and High Depression Score Range
Abstract
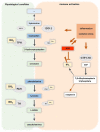
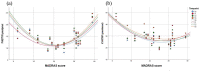
The immunomodulatory capacity of mental stress is one of the basic concepts of psychoneuroimmunology. The current prospective longitudinal study was designed to evaluate the effect of acute mental stress on neurotransmitter precursor amino acid levels in individuals with depression at 2 time points. Ten physically healthy patients with a diagnosis of major depressive episode and Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale scores (MADRAS) ⩾20 points at inclusion were assessed on 2 study days (once with higher MADRAS scores, once with lower MADRAS scores; median 34.5 days apart) and subjected to a standardized acute mental stress test on each study day. Blood was collected at 4 time points: once prior to and at 3 time points (0, 30 minutes, 60 minutes) following mental stress. Neurotransmitter precursor amino acid levels, that is kynurenine/tryptophan (KYN/TRP) and phenylalanine/tyrosine (PHE/TYR), as well as neopterin and nitrite were analyzed in a total of 80 individual blood samples. Regression and correlation analyses were performed. Regression analyses of PHE/TYR (R 2 = .547) and KYN/TRP (R 2 = .440) in relation to MADRAS depression severity showed a quadratic curve fit. This was reflected by a negative linear correlation between MADRAS scores and PHE/TYR as well as KYN/TRP in the lower score range (r = -.805, P < .001 and r = -.586, P < .001 respectively) and a positive correlation in the higher MADRAS score range (r = .713, P < .001 and r = .379, P = .016 respectively). No effect of acute mental stress was found. This analysis exemplifies the implications of sampling as well as data distributions on results. The crosstalk of biological mechanisms that orchestrate metabolic and immunological signaling may vary depending on depression severity resulting in non-linear associations that may explain the heterogeneity of results found in the literature.
Keywords: Depression severity; kynurenine; neurotransmitter; phenylalanine; quadratic curve fit; tryptophan; tyrosine.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration Of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Rush AJ, Trivedi MH, Wisniewski SR, et al. Acute and longer-term outcomes in depressed outpatients requiring one or several treatment steps: a STAR*D report. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163:1905-1917. - PubMed
-
- Turck CW.Biomarkers for Psychiatric Disorders. 1st ed. Springer; 2009.
-
- Padmos RC, Hillegers MH, Knijff EM, et al. A discriminating messenger RNA signature for bipolar disorder formed by an aberrant expression of inflammatory genes in monocytes. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2008;65:395-407. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

