Remdesivir and Cyclosporine Synergistically Inhibit the Human Coronaviruses OC43 and SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 34483914
- PMCID: PMC8409573
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.706901
Remdesivir and Cyclosporine Synergistically Inhibit the Human Coronaviruses OC43 and SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
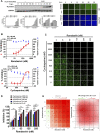
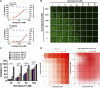
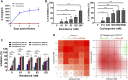
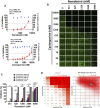
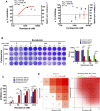
Remdesivir, a prodrug targeting RNA-dependent-RNA-polymerase, and cyclosporine, a calcineurin inhibitor, individually exerted inhibitory activity against human coronavirus OC43 (HCoV-OC43) in HCT-8 and MRC-5 cells at EC50 values of 96 ± 34 ∼ 85 ± 23 nM and 2,920 ± 364 ∼ 4,419 ± 490 nM, respectively. When combined, these two drugs synergistically inhibited HCoV-OC43 in both HCT-8 and MRC-5 cells assayed by immunofluorescence assay (IFA). Remdesivir and cyclosporine also separately reduced IL-6 production induced by HCoV-OC43 in human lung fibroblasts MRC-5 cells with EC50 values of 224 ± 53 nM and 1,292 ± 352 nM, respectively; and synergistically reduced it when combined. Similar trends were observed for SARS-CoV-2, which were 1) separately inhibited by remdesivir and cyclosporine with respective EC50 values of 3,962 ± 303 nM and 7,213 ± 143 nM by IFA, and 291 ± 91 nM and 6,767 ± 1,827 nM by a plaque-formation assay; and 2) synergistically inhibited by their combination, again by IFA and plaque-formation assay. Collectively, these results suggest that the combination of remdesivir and cyclosporine merits further study as a possible treatment for COVID-19 complexed with a cytokine storm.
Keywords: COVID-19; IL-6; IL-8; OC43; SARS-CoV-2; cyclosporine; remdesivir; synergistic.
Copyright © 2021 Hsu, Yang, Lee, Lin, Chang, Yang, Liang, Chao, Liao, Kao, Wu, Chang, Sytwu, Chen and Lee.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

