Enroll-HD: An Integrated Clinical Research Platform and Worldwide Observational Study for Huntington's Disease
- PMID: 34484094
- PMCID: PMC8416308
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.667420
Enroll-HD: An Integrated Clinical Research Platform and Worldwide Observational Study for Huntington's Disease
Abstract
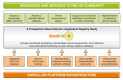
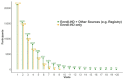
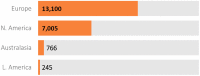
Established in July 2012, Enroll-HD is both an integrated clinical research platform and a worldwide observational study designed to meet the clinical research requirements necessary to develop therapeutics for Huntington's disease (HD). The platform offers participants a low-burden entry into HD research, providing a large, well-characterized, research-engaged cohort with associated clinical data and biosamples that facilitates recruitment into interventional trials and other research studies. Additional studies that use Enroll-HD data and/or biosamples are built into the platform to further research on biomarkers and outcome measures. Enroll-HD is now operating worldwide in 21 countries at 159 clinical sites across four continents-Europe, North America, Latin America, and Australasia-and has recruited almost 25,000 participants, generating a large, rich clinical database with associated biosamples to expedite HD research; any researcher at a verifiable research organization can access the clinical datasets and biosamples from Enroll-HD and nested studies. Important operational features of Enroll-HD include a strong emphasis on standardization, data quality, and protecting participant identity, a single worldwide study protocol, a flexible EDC system capable of integrating multiple studies, a comprehensive monitoring infrastructure, an online portal to train and certify site personnel, and standardized study documents including informed consent forms and contractual agreements.
Keywords: Enroll-HD; Huntington's disease; clinical research platform; disease network; longitudinal observational cohort study; registry.
Copyright © 2021 Sathe, Ware, Levey, Neacy, Blumenstein, Noble, Mühlbäck, Rosser, Landwehrmeyer and Sampaio.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

