Widespread Disruptions of White Matter in Familial Multiple Sclerosis: DTI and NODDI Study
- PMID: 34484098
- PMCID: PMC8415561
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.678245
Widespread Disruptions of White Matter in Familial Multiple Sclerosis: DTI and NODDI Study
Abstract
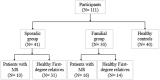
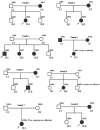
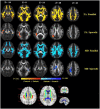
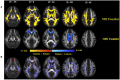
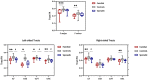
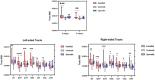
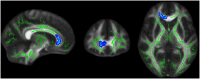
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is a noninvasive, quantitative MRI technique that measures white matter (WM) integrity. Many brain dimensions are heritable, including white matter integrity measured with DTI. Family studies are valuable to provide insights into the interactive effects of non-environmental factors on multiple sclerosis (MS). To examine the contribution of familial factors to the diffusion signals across WM microstructure, we performed DTI and calculated neurite orientation dispersion plus density imaging (NODDI) diffusion parameters in two patient groups comprising familial and sporadic forms of multiple sclerosis and their unaffected relatives. We divided 111 subjects (49 men and 62 women: age range 19-60) into three groups conforming to their MS history. The familial MS group included 30 participants (patients; n = 16, healthy relatives; n = 14). The sporadic group included 41 participants (patients; n = 10, healthy relatives; n = 31). Forty age-matched subjects with no history of MS in their families were defined as the control group. To study white matter integrity, two methods were employed: one for calculating the mean of DTI, FA, and MD parameters on 18 tracts using Tracts Constrained by Underlying Anatomy (TRACULA) and the other for whole brain voxel-based analysis using tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS) on NDI and ODI parameters derived from NODDI and DTI parameters. Voxel-based analysis showed considerable changes in FA, MD, NDI, and ODI in the familial group when compared with the control group, reflecting widespread impairment of white matter in this group. The analysis of 18 tracts with TRACULA revealed increased MD and FA reduction in more tracts (left and right ILF, UNC, and SLFT, forceps major and minor) in familial MS patients vs. the control group. There were no significant differences between the patient groups. We found no consequential changes in healthy relatives of both patient groups in voxel-based and tract analyses. Considering the multifactorial etiology of MS, familial studies are of great importance to clarify the effects of certain predisposing factors on demyelinating brain pathology.
Keywords: DTI; NODDI; TRACULA; brain mapping; familial multiple sclerosis.
Copyright © 2021 Gharaylou, Sahraian, Hadjighassem, Kohanpour, Doosti, Nahardani and Moghadasi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Neurite Orientation Dispersion and Density Imaging and Two-Compartment Spherical Mean Technique Parameter Maps in Multiple Sclerosis.Front Neurol. 2021 Jun 14;12:662855. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.662855. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34194382 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Microstructural Substrates of White Matter Abnormalities: A Comparative Study Using DTI and NODDI.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 21;11(12):e0167884. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167884. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 28002426 Free PMC article.
-
White matter microstructural disruption in minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging (NODDI) study.Neuroradiology. 2023 Nov;65(11):1589-1604. doi: 10.1007/s00234-023-03201-1. Epub 2023 Jul 24. Neuroradiology. 2023. PMID: 37486421
-
Investigating Microstructural Changes in White Matter in Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Neurite Orientation Dispersion and Density Imaging.Brain Sci. 2021 Aug 29;11(9):1151. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11091151. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 34573172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of diffusion tensor imaging and fractional anisotropy in the evaluation of patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a literature review.Neurosurg Focus. 2016 Sep;41(3):E12. doi: 10.3171/2016.6.FOCUS16192. Neurosurg Focus. 2016. PMID: 27581308 Review.
Cited by
-
Tract-based analyses of white matter in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, aging, and dementia using high spatial and directional resolution diffusion imaging: a pilot study.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Feb 1;15:1240502. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1240502. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38362028 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal fibre-specific white matter damage predicts cognitive decline in multiple sclerosis.Brain Commun. 2024 Jan 27;6(1):fcae018. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcae018. eCollection 2024. Brain Commun. 2024. PMID: 38344654 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of 3-month CPAP therapy on brain structure in obstructive sleep apnea: A diffusion tensor imaging study.Front Neurol. 2022 Aug 22;13:913193. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.913193. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36071900 Free PMC article.
-
Automated three-dimensional major white matter bundle segmentation using diffusion magnetic resonance imaging.Anat Sci Int. 2023 Jul;98(3):318-336. doi: 10.1007/s12565-023-00715-9. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Anat Sci Int. 2023. PMID: 37017902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disrupted topological properties of the structural brain network in patients with cerebellar infarction on different sides are associated with cognitive impairment.Front Neurol. 2022 Sep 20;13:982630. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.982630. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36203973 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

