Identification of a Nomogram from Ferroptosis-Related Long Noncoding RNAs Signature to Analyze Overall Survival in Patients with Bladder Cancer
- PMID: 34484338
- PMCID: PMC8413054
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8533464
Identification of a Nomogram from Ferroptosis-Related Long Noncoding RNAs Signature to Analyze Overall Survival in Patients with Bladder Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to establish a nomogram to predict the overall survival (OS) of patients with bladder cancer (BC) by ferroptosis-related long noncoding RNAs (FRlncRNAs) signature.
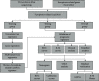
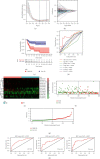
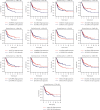
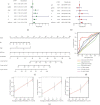
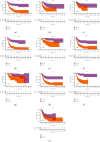
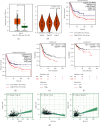
Methods: We obtained FRlncRNAs expression profiles and clinical data of patients with BC from the Cancer Genome Atlas database. The patients were divided into the training set, testing set, and overall set. Lasso regression and multivariate Cox regression were used to establish the FRlncRNAs signature, the prognosis of each group was compared by Kaplan-Meier (K-M) analysis, and the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve evaluated the accuracy of the model. The Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) was used for the visualization of the functional enrichment for FRlncRNAs. The databases of GEPIA and K-M Plotter were used for subsequent functional analysis of major FRlncRNAs.
Results: Thirteen prognostic FRlncRNAs (LINC00942, MAFG-DT, AL049840.3, AL136084.3, OCIAD1-AS1, AC062017.1, AC008074.2, AC018653.3, AL031775.1, USP30-AS1, LINC01767, AC132807.2, and AL354919.2) were identified to be significantly different, constituting an FRlncRNAs signature. Patients with BC were divided into low-risk group and high-risk group by this signature in the training, testing, and overall sets. K-M analysis showed that the prognosis of patients in the high-risk group was poor and the difference in the subgroup analyses was statistically significant. ROC analysis revealed that the predictive ability of the model was more accurate than traditional assessment methods. A risk score based on FRlncRNAs signature was an independent prognostic factor for the patients with BC (HR = 1.388, 95%CI = 1.228-1.568, P < 0.001). Combining the FRlncRNAs signature and clinicopathological factors, a predictive nomogram was constructed. The nomogram can accurately predict the overall survival of patients and had high clinical practicability. The GSEA analysis showed that the primary pathways were WNT, MAPK, and cell-matrix adhesion signaling pathways. The major FRlncRNAs (MAFG-DT) were associated with poor prognosis in the GEPIA and K-M Plotter database.
Conclusion: Thirteen prognostic FRlncRNAs and their nomogram were accurate tools for predicting the OS of BC, which might be molecular biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Copyright © 2021 Yuanshan Cui et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Soukup V., Čapoun O., Cohen D., et al. Prognostic performance and reproducibility of the 1973 and 2004/2016 world health organization grading classification systems in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: a European association of Urology non-muscle invasive bladder cancer guidelines panel systematic review. European Urology. 2017;72(5):801–813. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.04.015. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

