Study of amalgam-like particles by polarized light microscopy
- PMID: 34484599
- PMCID: PMC8403881
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jds.2021.06.009
Study of amalgam-like particles by polarized light microscopy
Keywords: Amalgam particle; Energy dispersive X-ray analysis; Polarized light microscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
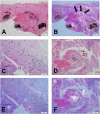
Figures
References
-
- Koppang H.S., Koppang R., Stolen S.O. Identification of common foreign material in postendodontic granulomas and cysts. J Dent Assoc S Afr. 1992;47:210–216. - PubMed
-
- Koppang H.S., Roushan A., Srafilzadeh A., Stolen S.O., Koppang R. Foreign body gingival lesions: distribution, morphology, identification by X-ray energy dispersive analysis and possible origin of foreign material. J Oral Pathol Med. 2007;36:161–172. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

