Injury Characteristics and Predisposing Effects of Various Outdoor Traumatic Situations in Children and Adolescents
- PMID: 34484636
- PMCID: PMC8380528
- DOI: 10.4055/cios20242
Injury Characteristics and Predisposing Effects of Various Outdoor Traumatic Situations in Children and Adolescents
Abstract
Backgroud: Many studies have reported injury characteristics of individual traumatic situations. However, a comparative analysis of specific risks is meaningful to better understand injury characteristics and help establish injury-prevention measures. This study was conducted to investigate and compare injury characteristics in children and adolescents by various outdoor traumatic situations.
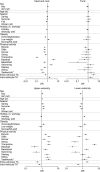
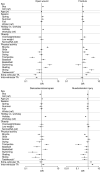
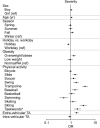
Methods: Outdoor traumatic situations were determined and classified into physical activity-related injury (n = 3,983) and pedestrian (n = 784) and passenger (n = 1,757) injuries in traffic accidents. Home injury (n = 16,121) was used as the control group. Then, the characteristics of each outdoor trauma were compared with 1:1 matched indoor trauma (among home injuries); each outdoor traumatic situation's predisposing risk for the injured body part, injury type, and injury severity were analyzed; and changes by age of frequency ranking among physical activity-related injuries were investigated.
Results: Outdoor trauma showed higher risks for limb injuries (injured body part), fracture and muscle/tendon injuries (injury type), and severe injuries (severity) than indoor trauma. Various outdoor traumatic situations presented different predisposing effects on injury characteristics. Among physical activity-related injuries, bicycle injury was commonest across all ages, and playing activities were common causes for injury for individuals of age < 9 years, whereas sports activities overwhelmed the common causes thereafter.
Conclusions: The findings would help to better understand the specific injury risk of various outdoor traumatic situations and may potentially facilitate the establishment of more effective injury-prevention measures.
Keywords: Adolescent; Children; Physical activity; Traffic accident; Trauma.
Copyright © 2021 by The Korean Orthopaedic Association.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Shanmugam C, Maffulli N. Sports injuries in children. Br Med Bull. 2008;86(1):33–57. - PubMed
-
- Maffulli N. The growing child in sport. Br Med Bull. 1992;48(3):561–568. - PubMed
-
- Li Q, Alonge O, Hyder AA. Children and road traffic injuries: can’t the world do better? Arch Dis Child. 2016;101(11):1063–1070. - PubMed
-
- Serinken M, Ozen M. Characteristics of injuries due to traffic accidents in the pediatric age group. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2011;17(3):243–247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

