Immune-Related Circulating miR-125b-5p and miR-99a-5p Reveal a High Recurrence Risk Group of Pancreatic Cancer Patients after Tumor Resection
- PMID: 34484811
- PMCID: PMC8415800
- DOI: 10.3390/app9224784
Immune-Related Circulating miR-125b-5p and miR-99a-5p Reveal a High Recurrence Risk Group of Pancreatic Cancer Patients after Tumor Resection
Abstract
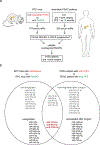
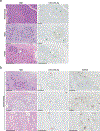
Clinical follow-up aided by changes in the expression of circulating microRNAs (miRs) may improve prognostication of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) patients. Changes in 179 circulating miRs due to cancer progression in the transgenic Kras G12D/+; Trp53 R172H/+; P48-Cre (KPC) animal model of PDAC were analyzed for serum miRs that are altered in metastatic disease. In addition, expression levels of 250 miRs were profiled before and after pancreaticoduodenectomy in the serum of two patients with resectable PDAC with different progression free survival (PFS) and analyzed for changes indicative of PDAC recurrence after resection. Three miRs that were upregulated ≥3-fold in progressive PDAC in both mice and patients were selected for validation in 26 additional PDAC patients before and after resection. We found that high serum miR-125b-5p and miR-99a-5p levels after resection are significantly associated with shorter PFS (HR 1.34 and HR 1.73 respectively). In situ hybridization for miR detection in the paired resected human PDAC tissues showed that miR-125b-5p and miR-99a-5p are highly expressed in inflammatory cells in the tumor stroma, located in clusters of CD79A expressing cells of the B-lymphocyte lineage. In conclusion, we found that circulating miR-125b-5p and miR-99a-5p are potential immune-cell related prognostic biomarkers in PDAC patients after surgery.
Keywords: biomarkers; circulating microRNAs; immune cells; pancreatic cancer; progression free survival; resection.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
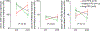

References
-
- Rahib L; Smith BD; Aizenberg R; Rosenzweig AB; Fleshman JM; Matrisian LM Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: The unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the united states. Cancer Res 2014, 74, 2913–2921. - PubMed
-
- Luberice K; Downs D; Sadowitz B; Ross S; Rosemurgy A Has survival improved following resection for pancreatic adenocarcinoma? Am. J. Surg 2017, 214, 341–346. - PubMed
-
- Van Rijssen LB; Koerkamp BG; Zwart MJ; Bonsing BA; Bosscha K; van Dam RM; van Eijck CH; Gerhards MF; van der Harst E; de Hingh IH; et al. Nationwide prospective audit of pancreatic surgery: Design, accuracy, and outcomes of the Dutch Pancreatic Cancer Audit. HPB 2017, 19, 919–926. - PubMed
-
- Van Roessel S; Mackay TM; Tol J; van Delden OM; van Lienden KP; Nio CY; Phoa S; Fockens P; van Hooft JE; Verheij J; et al. Impact of expanding indications on surgical and oncological outcome in 1434 consecutive pancreatoduodenectomies. HPB 2019, 21, 865–875. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
