Integrated analysis of the rhesus monkey liver transcriptome during development and human primary HCC AFP-related gene expression
- PMID: 34484865
- PMCID: PMC8403716
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.06.004
Integrated analysis of the rhesus monkey liver transcriptome during development and human primary HCC AFP-related gene expression
Abstract
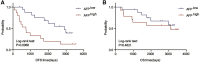
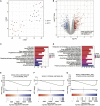
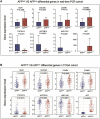
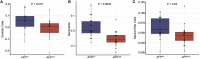
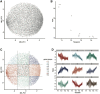
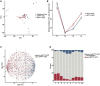
Embryonic development and tumorigenesis have a certain degree of similarity. Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), a protein related to embryonic development, is a well-known biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In this study, we analyzed the differences in gene expression profiles and molecular mechanisms in human HCC tissues from patients in AFPhigh (serum AFP level ≥ 25 ng/mL) and AFPlow (serum AFP level < 25 ng/mL) groups. The results indicated that AFPhigh HCC has more malignant biological characteristics. Single-sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA) showed significantly higher levels of genes expressed in dendritic cells, neutrophils, and natural killer cells in the AFPlow group than in the AFPhigh group. Then, we defined a rhesus monkey fetal liver developmental landscape and compared it to the HCC gene expression profile. The gene signatures of AFPhigh HCC tissues were similar to those of early embryonic liver tissues. In this study, we comprehensively analyzed the rhesus monkey liver transcriptome during development and human primary HCC AFP-related gene expression profiles and clarified the function of AFP in the occurrence and development of HCC from the perspective of developmental biology, which might provide a new perspective on the pathogenesis of HCC.
Keywords: AFP; embryonic liver development; hepatocellular carcinoma; rhesus monkey; tumor immunity.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Wallace M.C., Preen D., Jeffrey G.P., Adams L.A. The evolving epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: a global perspective. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015;9:765–779. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

