Containing the Transmission of COVID-19: A Modeling Study in 160 Countries
- PMID: 34485337
- PMCID: PMC8416347
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.701836
Containing the Transmission of COVID-19: A Modeling Study in 160 Countries
Abstract
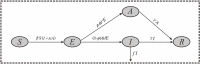
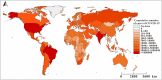
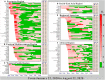
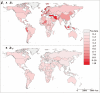
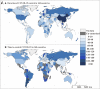
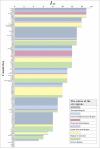
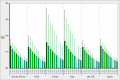
Background: It is much valuable to evaluate the comparative effectiveness of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) prevention and control in the non-pharmacological intervention phase of the pandemic across countries and identify useful experiences that could be generalized worldwide. Methods: In this study, we developed a susceptible-exposure-infectious-asymptomatic-removed (SEIAR) model to fit the daily reported COVID-19 cases in 160 countries. The time-varying reproduction number (R t ) that was estimated through fitting the mathematical model was adopted to quantify the transmissibility. We defined a synthetic index (I AC ) based on the value of R t to reflect the national capability to control COVID-19. Results: The goodness-of-fit tests showed that the SEIAR model fitted the data of the 160 countries well. At the beginning of the epidemic, the values of R t of countries in the European region were generally higher than those in other regions. Among the 160 countries included in the study, all European countries had the ability to control the COVID-19 epidemic. The Western Pacific Region did best in continuous control of the epidemic, with a total of 73.76% of countries that can continuously control the COVID-19 epidemic, while only 43.63% of the countries in the European Region continuously controlled the epidemic, followed by the Region of Americas with 52.53% of countries, the Southeast Asian Region with 48% of countries, the African Region with 46.81% of countries, and the Eastern Mediterranean Region with 40.48% of countries. Conclusion: Large variations in controlling the COVID-19 epidemic existed across countries. The world could benefit from the experience of some countries that demonstrated the highest containment capabilities.
Keywords: COVID-19; epidemic; mathematical model; the effective reproduction number; transmissibility.
Copyright © 2021 Niu, Rui, Wang, Zhang, Chen, Xie, Zhao, Lin, Zhu, Wang, Xu, Liu, Yang, Zheng, Chen, Xia, Xu, Zhang, Ji, Jin, Chen, Zhao, Su, Song, Chen and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zhao S, Lin Q, Ran J, Musa SS, Yang G, Wang W, et al. Preliminary estimation of the basic reproduction number of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in China, from 2019 to 2020: A data-driven analysis in the early phase of the outbreak. Int J Infect Dis. (2020) 92:214–7. 10.1101/2020.01.23.916395 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- I.L. Organization . Almost 25 million jobs could be lost worldwide as a result of COVID-19, Says ILO. (2020). Available online at: https://www.ilo.org/hanoi/Informationresources/Publicinformation/Pressre...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

