An overview of 2019 novel coronavirus COVID-19 pandemic: A review study
- PMID: 34485577
- PMCID: PMC8395953
- DOI: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_1403_20
An overview of 2019 novel coronavirus COVID-19 pandemic: A review study
Erratum in
-
Erratum: An overview of 2019 novel coronavirus COVID-19 pandemic: A review study.J Educ Health Promot. 2021 Aug 31;10:323. doi: 10.4103/2277-9531.324920. eCollection 2021. J Educ Health Promot. 2021. PMID: 34667823 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, was first reported in December 2019 in Wuhan, Hubei province, China. It is now known as a pandemic and a global crisis due to rapid human-to-human transmission with the vast expansion that has affected almost all countries. The primary source of the disease is still unknown, but it is possible that the virus was transmitted through bat to an intermediate host and then to humans. The main and early symptoms of COVID-19 infection are fatigue, fever, dry cough, myalgia, and dyspnea. The incubation period of the disease is about 2-14 days, which is one of the important parameters for planning to prevent disease outbreak. PT-polymerase chain reaction test is used to diagnose the disease; chest computed tomography scan, chest X-ray, blood tests, and symptoms are also very helpful in diagnosing the disease. There is a strong emphasis on controlling infections and hand hygiene to prevent the transmission of the disease. There is not enough knowledge about this disease yet, and there are no specific vaccines or medications available to prevent and treat this disease. The current review study uses articles indexed on databases of Embase, Elsevier, PubMed, and World Health Organization and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and keywords of coronavirus, COVID-19, acute respiratory distress syndrome and China.
Keywords: COVID-19; Infectious disease; SARS-CoV-2; epidemic; health emergency; novel coronavirus; pandemic; review.
Copyright: © 2021 Journal of Education and Health Promotion.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
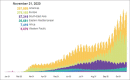
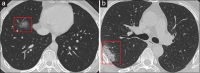
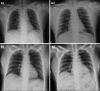
References
-
- Jalilian N, Ziapour A, Mokari Z, Kianipour N. A study of the relationship between the components of spiritual health and happiness of students at Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences in 2016. Ann Trop Med Public Health. 2017;10:1010–4.
-
- Yoosefi Lebni Y, Abbas J, Moradi F, Salahshoor MR, Chaboksavar F, Irandoost SF, et al. How the COVID-19 pandemic effected economic, social, political, and cultural factors: A lesson from Iran. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2020. pp. 1–3. In Press. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/100.1177/0020764020939984 . - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

