Comparison of a Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection and a Conventional Steroid Injection for Pain Relief and Functional Improvement of Partial Supraspinatus Tears
- PMID: 34485587
- PMCID: PMC8414632
- DOI: 10.1177/23259671211024937
Comparison of a Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection and a Conventional Steroid Injection for Pain Relief and Functional Improvement of Partial Supraspinatus Tears
Abstract
Background: Partial supraspinatus tendon tears have frequently been treated using a subacromial corticosteroid injection or surgery. The clinical use of a platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injection is an alternative treatment method for the condition, despite the paucity of evidence of its efficacy.
Purpose: To compare pain relief, functional improvement, and complications after an intratendinous PRP injection versus a subacromial corticosteroid injection for partial supraspinatus tears.
Study design: Randomized controlled trial; Level of evidence, 1.
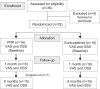
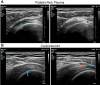
Methods: A total of 32 patients with partial supraspinatus tears were randomly assigned to receive a leukocyte-poor PRP (LP-PRP) injection or a corticosteroid injection. One patient withdrew from the PRP group, leaving 15 patients in the PRP group and 16 patients in the corticosteroid group. The ultrasound-guided procedures were performed by a single experienced pain physician. Pain relief and functional improvement were evaluated using the visual analog scale (VAS) and the Oxford Shoulder Score (OSS), respectively. Treatment efficacy and complications were documented, and the 2 groups were compared at 1- and 6-month follow-up.
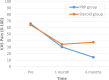
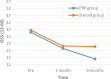
Results: There were no differences in VAS and OSS scores between the PRP and corticosteroid groups at 1-month follow-up. However, the PRP group had better scores than the corticosteroid group had on both the VAS and OSS at 6-month follow-up (VAS: 14.5 ± 15.4 vs 37.5 ± 24.9, respectively; OSS: 16.2 ± 3.9 vs 25.0 ± 10.2, respectively; P < .01 for both). Both groups showed significant improvement in VAS and OSS scores from before treatment to 1-month follow-up (mean difference, 35.67 and 11.47 points, respectively, for the PRP group; mean difference, 29.69 and 11.13 points, respectively, for the corticosteroid group; P < .01 for all). The VAS and OSS scores did not change significantly at 6-month follow-up in the corticosteroid group; however, the PRP group showed continued improvement in both VAS and OSS scores between 1- and 6-month follow-up (mean difference, 15.87 and 7.40 points, respectively; P < .01 for both). There were no complications in either group.
Conclusion: An injection using either a corticosteroid or LP-PRP resulted in a similar reduction in pain and improvement in function at 1 month in patients with a partial supraspinatus tear. However, PRP showed superior benefits over the corticosteroid at 6-month follow-up.
Keywords: pain intervention; platelet-rich plasma; rotator cuff tear; supraspinatus tear.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
One or more of the authors has declared the following potential conflict of interest or source of funding: This study received funding support from the Pain Management Research Unit, Department of Anesthesiology, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University. AOSSM checks author disclosures against the Open Payments Database (OPD). AOSSM has not conducted an independent investigation on the OPD and disclaims any liability or responsibility relating thereto.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A systematic review of randomized control trials looking at functional improvement of rotator cuff partial thickness tears following platelet-rich-plasma injection: a comparison of glenohumeral joint vs. subacromial bursa vs. intratendinous injection locations.JSES Int. 2024 Jan 24;8(3):464-471. doi: 10.1016/j.jseint.2024.01.003. eCollection 2024 May. JSES Int. 2024. PMID: 38707549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subacromial injection of platelet-rich plasma provides greater improvement in pain and functional outcomes compared to corticosteroids at 1-year follow-up: a double-blinded randomized controlled trial.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2024 Dec;33(12):2563-2571. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2024.06.012. Epub 2024 Aug 3. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2024. PMID: 39098382 Clinical Trial.
-
Role of Image-guided Platelet-rich Plasma Injection in the Management of Patients of Supraspinatus Tendon Tear.J Orthop Case Rep. 2024 Dec;14(12):257-262. doi: 10.13107/jocr.2024.v14.i12.5090. J Orthop Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39669014 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparative study on effectiveness of injecting platelet-rich plasma with different concentrations of leukocytes under ultrasound in treatment of supraspinatus tendon injury].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Dec 15;38(12):1445-1450. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202408094. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39694833 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Platelet-rich plasma versus hyaluronic acid in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Sep 11;15(1):403. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-01919-9. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 32912243 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Platelet-rich plasma does not improve clinical results in patients with rotator cuff disorders but reduces the retear rate. A systematic review and meta-analysis.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023 May;31(5):1940-1952. doi: 10.1007/s00167-022-07223-9. Epub 2022 Dec 11. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023. PMID: 36496450
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection in Non-Operative Treatment of Partial-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Rehabil Med. 2022 Sep 16;54:jrm00312. doi: 10.2340/jrm.v54.1434. J Rehabil Med. 2022. PMID: 35892292 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-rich plasma and corticosteroid injection for tendinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Apr 8;26(1):339. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08566-3. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40200209 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical application of ultrasound-guided platelet-rich plasma gel in the treatment of supraspinatus tendon tears: a single-center retrospective study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 14;15(1):25427. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09595-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40659708 Free PMC article.
-
All-Inside Arthroscopic Partial Articular-Sided Supraspinatus Tendon Avulsion (PASTA) Repair Without Bunching of the Bursal Side of the Tendon.Arthrosc Tech. 2022 May 21;11(6):e1071-e1075. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2022.02.013. eCollection 2022 Jun. Arthrosc Tech. 2022. PMID: 35782853 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abate M, Salini V, Schiavone C, Andia I. Clinical benefits and drawbacks of local corticosteroids injections in tendinopathies. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017;16(3):341–349. - PubMed
-
- Akan O, Mete B, Koçyiğit H, Bayram KB, Yilmaz HE, Tosun A. Efficacy of ultrasound guided platelet-rich plasma in the repair of partial and full-thickness supraspinatus tears. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2019;12(9):11.
-
- Alfredson H. Chronic midportion Achilles tendinopathy: an update on research and treatment. Clin Sports Med. 2003;22(4):727–741. - PubMed
-
- Andia I, Latorre PM, Gomez MC, Burgos-Alonso N, Abate M, Maffulli N. Platelet-rich plasma in the conservative treatment of painful tendinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled studies. Br Med Bull. 2014;110(1):99–115. - PubMed
-
- Balasubramaniam U, Dissanayake R, Annabell L. Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma injections in pain associated with chronic tendinopathy: a systematic review. Phys Sportsmed. 2015;43(3):253–261. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

