Multisensory Facilitation of Working Memory Training
- PMID: 34485810
- PMCID: PMC8415034
- DOI: 10.1007/s41465-020-00196-y
Multisensory Facilitation of Working Memory Training
Abstract
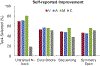
Research suggests that memorization of multisensory stimuli benefits performance compared to memorization of unisensory stimuli; however, little is known about multisensory facilitation in the context of working memory (WM) training and transfer. To investigate this, 240 adults were randomly assigned to an N-back training task that consisted of visual-only stimuli, alternating visual and auditory blocks, or audio-visual (multisensory) stimuli, or to a passive control group. Participants in the active groups completed 13 sessions of N-back training (6.7 hours in total) and all groups completed a battery of WM tasks: untrained N-back tasks, Corsi Blocks, Sequencing, and Symmetry Span. The Multisensory group showed similar training N-level gain compared to the Visual Only group, and both of these groups outperformed the Alternating group on the training task. As expected, all three active groups significantly improved on untrained visual N-back tasks compared to the Control group. In contrast, the Multisensory group showed significantly greater gains on the Symmetry Span task and to a certain extent on the Sequencing task compared to other groups. These results tentatively suggest that incorporating multisensory objects in a WM training protocol can benefit performance on the training task and potentially facilitate transfer to complex WM span tasks.
Keywords: multisensory; training; transfer; working memory.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

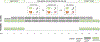


References
-
- Boot WR, Simons DJ, Stothart C, & Stutts C (2013). The Pervasive Problem With Placebos in Psychology: Why Active Control Groups Are Not Sufficient to Rule Out Placebo Effects. Perspectives on Psychological Science : A Journal of the Association for Psychological Science, 8(4), 445–454. doi: 10.1177/1745691613491271 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
