Colloidal dispersion of poly(ionic liquid)/Cu composite particles for protective surface coating against SAR-CoV-2
- PMID: 34485979
- PMCID: PMC8242609
- DOI: 10.1002/nano.202100069
Colloidal dispersion of poly(ionic liquid)/Cu composite particles for protective surface coating against SAR-CoV-2
Abstract
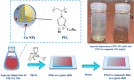
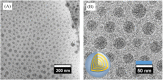
Herein, we report a waterproof anti-SARS-CoV-2 protective film prepared by spray-coating of an aqueous colloidal dispersion of poly(ionic liquid)/copper (PIL/Cu) composite nanoparticles onto a substrate. The PIL dispersion was prepared by suspension polymerization of 3-dodecyl-1-vinylimdiazolium bromide in water at 70°C. The copper acetate salt was added into the PIL nanoparticle dispersion and in situ reduced into copper nanoparticles anchoring onto the PIL nanoparticles. Despite being waterborne, the PIL in bulk is intrinsically insoluble in water and the formed coating is stable in water. The formed surface coating by PIL/copper composite nanoparticles was able to deactivate SARS-CoV-2 virions by 90.0% in 30 minutes and thus may effectively prevent the spread of SARS-CoV-2 through surface contact. This method may provide waterborne dispersions for a broad range of antivirus protective surface coatings for both outdoor and indoor applications.
Keywords: SARS‐CoV‐2; antivirus coating; colloidal dispersion; copper nanoparticle; poly(ionic liquid).
© 2021 The Authors. Nano Select published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Figures
References
-
- Rai P. K., Usmani Z., Thakur V. K., Gupta V. K., Mishra Y. K., Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 3, 100011.
-
- Talebian S., Wallace G. G., Schroeder A., Stellacci F., Conde J., Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 618. - PubMed
-
- Sun Z., Ostrikov K. (Ken), Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2020, 25, e00203.
-
- Das Jana I., Kumbhakar P., Banerjee S., Gowda C. C., Kedia N., Kuila S. K., Banerjee S., Das N. C., Das A. K., Manna I., Tiwary C. S., Mondal A., ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 352.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
