Inactivation of RNase P in Escherichia coli significantly changes post-transcriptional RNA metabolism
- PMID: 34486768
- PMCID: PMC8766891
- DOI: 10.1111/mmi.14808
Inactivation of RNase P in Escherichia coli significantly changes post-transcriptional RNA metabolism
Abstract
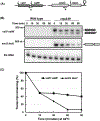
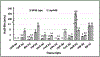
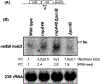
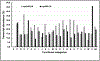
Ribonuclease P (RNase P), which is required for the 5'-end maturation of tRNAs in every organism, has been shown to play a limited role in other aspects of RNA metabolism in Escherichia coli. Using RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq), we demonstrate that RNase P inactivation affects the abundances of ~46% of the expressed transcripts in E. coli and provide evidence that its essential function is its ability to generate pre-tRNAs from polycistronic tRNA transcripts. The RNA-seq results agreed with the published data and northern blot analyses of 75/83 transcripts (mRNAs, sRNAs, and tRNAs). Changes in transcript abundances in the RNase P mutant also correlated with changes in their half-lives. Inactivating the stringent response did not alter the rnpA49 phenotype. Most notably, increases in the transcript abundances were observed for all genes in the cysteine regulons, multiple toxin-antitoxin modules, and sigma S-controlled genes. Surprisingly, poly(A) polymerase (PAP I) modulated the abundances of ~10% of the transcripts affected by RNase P. A comparison of the transcriptomes of RNase P, RNase E, and RNase III mutants suggests that they affect distinct substrates. Together, our work strongly indicates that RNase P is a major player in all aspects of post-transcriptional RNA metabolism in E. coli.
Keywords: genome-wide RNA-seq; polyadenylation; sRNA; transcriptome.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures








References
-
- Alifano P, Rivellini F, Piscitelli C, Arraiano CM, Bruni CB, and Carlomagno MS (1994). Ribonuclease E provides substrates for ribonuclease P-dependent processing of a polycistronic mRNA. Genes Dev 8, 3021–3031. - PubMed
-
- Altuvia S, Weinstein-Fischer D, Zhang A, Postow L, and Storz G (1997). A small, stable RNA induced by oxidative stress: role as a pleiotropic regulator and antimutator. Cell 90, 43–53. - PubMed
-
- August J, Ortiz PJ, and Hurwitz J (1962). Ribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleotide incorporation. I. Purification and properties of the enzyme. J Biol Chem 237, 3786–3793. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

