A simple prognostic score based on troponin and presepsin for COVID-19 patients admitted to the emergency department: a single-center pilot study
- PMID: 34487072
- PMCID: PMC8477102
- DOI: 10.23750/abm.v92i4.11479
A simple prognostic score based on troponin and presepsin for COVID-19 patients admitted to the emergency department: a single-center pilot study
Abstract
Background: The need to determine prognostic factors that can predict a particularly severe or, conversely, the benign course of COVID-19 is particularly perceived in the Emergency Department (ED), considering the scarcity of resources for a conspicuous mass of patients. The aim of our study was to identify some predictors for 30-day mortality among some clinical, laboratory, and ultrasound variables in a COVID-19 patients population.
Methods: Prospective single-center pilot study conducted in an ED of a University Hospital. A consecutive sample of confirmed COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory failure was enrolled from March 8th to April 15th, 2020.
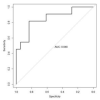
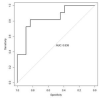
Results: 143 patients were enrolled. Deceased patients (n = 65) were older (81 vs. 61 years, p <0.001), and they had more frequently a history of heart disease, neurological disease, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (p-values = 0.026, 0.025, and 0.034, respectively) than survived patients. Troponin I and presepsin had a significant correlation with a worse outcome. Troponin achieved a sensitivity of 77% and a specificity of 82% for a cut-off value of 27.6 ng/L. The presepsin achieved a sensitivity of 54% and a specificity of 92% for a cut-off value of 871 pg/mL.
Conclusion: In a population of COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory failure in an ED, presepsin and troponin I are accurate predictors of 30-day mortality. Presepsin is highly specific and could permit the early identification of patients who could benefit from more intensive care as soon as they enter the ED. Further validation studies are needed to confirm this result.
Conflict of interest statement
Each author declares that he or she has no commercial associations (e.g. consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangement etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

