Impact of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic on patients with lysosomal storage disorders and restoration of services: experience from a specialist centre
- PMID: 34487419
- PMCID: PMC8652804
- DOI: 10.1111/imj.15473
Impact of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic on patients with lysosomal storage disorders and restoration of services: experience from a specialist centre
Abstract
This study aims to evaluate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the lysosomal disorders unit (LSDU) at Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust (RFL), a highly specialised national service for diagnosis and management of adults with lysosomal storage disorders (LSD). Review of home care enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) and emergency care, and COVID-19 shielding categories as per UK government guidance. New clinical pathways were developed to manage patients safely during the pandemic; staff well-being initiatives are described. LSDU staff were redeployed and/or had additional roles to support increased needs of hospitalised COVID-19 patients. During the first lockdown in March 2020, 286 of 602 LSD patients were shielding; 72 of 221 had home care ERT infusions interrupted up to 12 weeks. During the pandemic, there was a 3% reduction in home care nursing support required, with patients learning to self-cannulate or require support for cannulation only. There were no increased adverse clinical events during this period. Twenty-one contracted COVID-19 infection, with one hospitalised and no COVID-19 related deaths. In 2020, virtual clinics were increased by 88% (video and/or telephone) compared to 2019. RFL well-being initiatives supported all staff. We provide an overview of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on staff and patients attending a highly specialised rare disease service. As far as we are aware, this is the first detailed narrative on the challenges and subsequent rapid adaptations made, both as part of a large organisation and as a specialist centre. Lessons learnt could be translated to other rare disease services and ensure readiness for any future pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; enzyme replacement therapy; lysosomal storage disorder; outpatient; restoration.
© 2021 The Authors. Internal Medicine Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Royal Australasian College of Physicians.
Figures
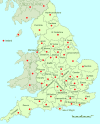
 ), high risk (red); (
), high risk (red); ( ), intermediate risk (amber); (
), intermediate risk (amber); ( ), low risk (green).
), low risk (green).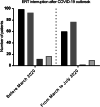
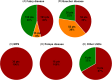
 ), Gaucher disease; (
), Gaucher disease; ( ), Fabry disease; (
), Fabry disease; ( ), Pompe disease; (
), Pompe disease; ( ), MPS. X‐axis: disease types; Y‐axis: percentage of patients on home care ERT.
), MPS. X‐axis: disease types; Y‐axis: percentage of patients on home care ERT.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD), U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Pandemic (H1N1 virus). 1918 [cited 2021 May 3]. Available from URL: https://www.cdc.gov/flu/pandemic-resources/1918-pandemic-h1n1.html
-
- Worldometer . [cited 2021 Apr 15]. Available from URL: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
-
- Platt FM. Sphingolipid lysosomal storage disorders. Nature 2014; 510: 68–75. - PubMed
-
- Meikle PJ, Hopwood JJ, Clague AE, Carey WF. Prevelance of lysosomal disorders. JAMA 1999; 281: 249–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

