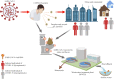
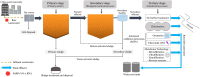
A review on detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater in light of the current knowledge of treatment process for removal of viral fragments
- PMID: 34488114
- PMCID: PMC8373619
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113563
A review on detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater in light of the current knowledge of treatment process for removal of viral fragments
Abstract
The entire globe is affected by the novel disease of coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19 or 2019-nCoV), which is formally recognised as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The World Health Organisation (WHO) announced this disease as a global pandemic. The presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in unprocessed wastewater has become a cause of worry due to these emerging pathogens in the process of wastewater treatment, as reported in the present study. This analysis intends to interpret the fate, environmental factors and route of transmission of SARS-CoV-2, along with its eradication by treating the wastewater for controlling and preventing its further spread. Different recovery estimations of the virus have been depicted by the detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater through the viral concentration techniques. Most frequently used viral concentration techniques include polyethylene glycol (PEG) precipitation, ultrafiltration, electronegative membrane, and ultracentrifugation, after which the detection and quantification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA are done in wastewater samples through quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) holds the key responsibility of eliminating pathogens prior to the discharge of wastewater into surface water bodies. The removal of SARS-CoV-2 RNA at the treatment stage is dependent on the operations of wastewater treatment systems during the outbreak of the virus; particularly, in the urban and extensively populated regions. Efficient primary, secondary and tertiary methods of wastewater treatment and disinfection can reduce or inactivate SARS-CoV-2 RNA before being drained out. Nonetheless, further studies regarding COVID-19-related disinfectants, environment conditions and viral concentrations in each treatment procedure, implications on the environment and regular monitoring of transmission need to be done urgently. Hence, monitoring the SARS-CoV-2 RNA in samples of wastewater under the procedure of wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) supplement the real-time data pertaining to the investigation of the COVID-19 pandemic in the community, regional and national levels.
Keywords: Disinfection; Surveillance; Transmission routes; Untreated wastewater; Virus concentration method; Wastewater treatment process; Wastewater–based epidemiology (WBE).
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that he has no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the methods for isolation and detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in municipal wastewater.Front Public Health. 2023 Mar 7;11:1116636. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1116636. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36960362 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 in environmental perspective: Occurrence, persistence, surveillance, inactivation and challenges.Chem Eng J. 2021 Feb 1;405:126893. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126893. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Chem Eng J. 2021. PMID: 32901196 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in commercial passenger aircraft and cruise ship wastewater: a surveillance tool for assessing the presence of COVID-19 infected travellers.J Travel Med. 2020 Aug 20;27(5):taaa116. doi: 10.1093/jtm/taaa116. J Travel Med. 2020. PMID: 32662867 Free PMC article.
-
Minimizing errors in RT-PCR detection and quantification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA for wastewater surveillance.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Jan 20;805:149877. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149877. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 34818780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater: State of the knowledge and research needs.Sci Total Environ. 2020 Oct 15;739:139076. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139076. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Sci Total Environ. 2020. PMID: 32758929 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Can spike fragments of SARS-CoV-2 induce genomic instability and DNA damage in the guppy, Poecilia reticulate? An unexpected effect of the COVID-19 pandemic.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Jun 15;825:153988. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153988. Epub 2022 Feb 19. Sci Total Environ. 2022. Retraction in: Sci Total Environ. 2024 Dec 20;957:177654. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.177654. PMID: 35192827 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
An opinion on Wastewater-Based Epidemiological Monitoring (WBEM) with Clinical Diagnostic Test (CDT) for detecting high-prevalence areas of community COVID-19 Infections.Curr Opin Environ Sci Health. 2022 Oct 6:100396. doi: 10.1016/j.coesh.2022.100396. Online ahead of print. Curr Opin Environ Sci Health. 2022. PMID: 36320818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Silico Assessment of Chemical Disinfectants on Surface Proteins Unveiled Dissimilarity in Antiviral Efficacy and Suitability towards Pathogenic Viruses.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 30;25(11):6009. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116009. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892197 Free PMC article.
-
Preparing for Mpox Resurgence: Surveillance Lessons From Outbreaks in Toronto, Canada.J Infect Dis. 2024 Mar 26;229(Supplement_2):S305-S312. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad533. J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38035826 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 and Water Variables: Review and Scientometric Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 5;20(2):957. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20020957. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36673718 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abu Ali H., Yaniv K., Bar-Zeev E., Chaudhury S., Shagan M., Lakkakula S., Ronen Z., Kushmaro A., Nir O. Tracking SARS-CoV-2 RNA through the wastewater treatment process. ACS ES&T Water. 2021;1:1161–1167. http://doi:10.1021/acsestwater.0c00216 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Agrawal S., Orschler L., Lackner S. Long-term monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater of the Frankfurt metropolitan area in Southern Germany. Sci. Rep. 2021;11:5372. http://doi:10.1038/s41598-021-84914-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed W., Bertsch P.M., Bibby K., Haramoto E., Hewitt J., Huygens F., Gyawali P., Korajkic A., Riddell S., Sherchan S.P., Simpson S.L., Sirikanchana K., Symonds E.M., Verhagen R., Vasan S.S., Kitajima M., Bivins A. Decay of SARS-CoV-2 and surrogate murine hepatitis virus RNA in untreated wastewater to inform application in wastewater-based epidemiology. Environ. Res. 2020;191 doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.110092. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed W., Angel N., Edson J., Bibby K., Bivins A., O'Brien J.W., Choi P.M., Kitajima M., Simpson S.L., Li J., Tscharke B., Verhagen R., Smith W.J.M., Zaugg J., Dierens L., Hugenholtz P., Thomas K.V., Mueller J.F. First confirmed detection of SARS- CoV-2 in untreated wastewater in Australia: a proof of concept for the wastewater surveillance of COVID-19 in the community. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;728 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138764. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed W., Bertsch P.M., Bivins A., Bibby K., Farkas K., Gathercole A., Haramoto E., Gyawali P., Korajkic A., McMinn B.R., Mueller J.F., Simpson S.L., Smith W.J.M., Symonds E.M., Thomas K.V., Verhagen R., Kitajima M. Comparison of virus concentration methods for the RT-qPCR-based recovery of murine hepatitis virus, a surrogate for SARS-CoV-2 from untreated wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;739 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139960. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous