Pinocembrin ameliorates post-infarct heart failure through activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 34488618
- PMCID: PMC8422663
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-021-00363-7
Pinocembrin ameliorates post-infarct heart failure through activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Oxidative stress is an important factor involved in the progress of heart failure. The current study was performed to investigate whether pinocembrin was able to ameliorate post-infarct heart failure (PIHF) and the underlying mechanisms.
Methods: Rats were carried out left anterior descending artery ligation to induce myocardial infarction and subsequently raised for 6 weeks to produce chronic heart failure. Then pinocembrin was administrated every other day for 2 weeks. The effects were evaluated by echocardiography, western blot, Masson's staining, biochemical examinations, immunohistochemistry, and fluorescence. In vitro we also cultured H9c2 cardiomyocytes and cardiac myofibroblasts to further testify the mechanisms.
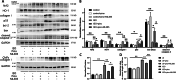
Results: We found that PIHF-induced deteriorations of cardiac functions were significantly ameliorated by administrating pinocembrin. In addition, the pinocembrin treatment also attenuated collagen deposition and augmented vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 in infarct border zone along with an attenuated apoptosis, which were related to an amelioration of oxidative stress evidenced by reduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in heart tissue and malondialdehyde (MDA) in serum, and increase of superoxide dismutase (SOD). This were accompanied by upregulation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/ heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) pathway. In vitro experiments we found that specific Nrf2 inhibitor significantly reversed the effects resulted from pinocembrin including antioxidant, anti-apoptosis, anti-fibrosis and neovascularization, which further indicated the amelioration of PIHF by pinocembrin was in a Nrf2/HO-1 pathway-dependent manner.
Conclusion: Pinocembrin ameliorated cardiac functions and remodeling resulted from PIHF by ROS scavenging and Nrf2/HO-1 pathway activation which further attenuated collagen fibers deposition and apoptosis, and facilitated angiogenesis.
Keywords: Heart failure; Nrf2/HO-1; Oxidative stress; Pinocembrin.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

