Frequency and predisposing factors for canine otitis externa in the UK - a primary veterinary care epidemiological view
- PMID: 34488894
- PMCID: PMC8422687
- DOI: 10.1186/s40575-021-00106-1
Frequency and predisposing factors for canine otitis externa in the UK - a primary veterinary care epidemiological view
Abstract
Background: Otitis externa is a commonly diagnosed disorder in dogs and can carry a high welfare impact on affected animals. This study aimed to report the prevalence and explore the role of breed and aural conformation as predisposing factors for canine otitis externa in the UK. The study used a cohort design of dogs under UK primary veterinary care at clinics participating in the VetCompass Programme during 2016. Risk factor analysis used multivariable logistic regression modelling.
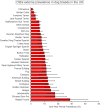
Results: The study included a random sample of 22,333 dogs from an overall population of 905,554 dogs under veterinary care in 2016. The one-year period prevalence of otitis externa was 7.30% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 6.97 to 7.65). Breed and ear carriage were the highest ranked risk factors. Compared with crossbred dogs, sixteen breed types showed increased odds, including: Basset Hound (odds ratio [OR] 5.87), Chinese Shar Pei (OR 3.44), Labradoodle (OR 2.95), Beagle (OR 2.54) and Golden Retriever (OR 2.23). Four breeds showed protection (i.e. reduced odds) of otitis externa: Chihuahua (OR 0.20), Border Collie (OR 0.34), Yorkshire Terrier (OR 0.49) and Jack Russell Terrier (OR 0.52). Designer breed types overall had 1.63 times the odds (95% CI 1.31 to 2.03) compared with crossbred dogs. Compared with breeds with erect ear carriage, breeds with pendulous ear carriage had 1.76 times the odds (95% CI 1.48 to 2.10) and breeds with V-shaped drop ear carriage had 1.84 times the odds (95% CI 1.53 to 2.21) of otitis externa.
Conclusions: Breed itself and breed-associated ear carriage conformation are important predisposing factors for canine otitis externa. Greater awareness of these associations for both predisposed and protected breeds could support veterinary practitioners to promote cautious and low-harm approaches in their clinical advice on preventive care for otitis externa, especially in predisposed breeds.
Keywords: Breed; Dog; Electronic patient record; Epidemiology; Erect ear; Pendulous ear; Primary-care; Purebred; VetCompass.
Plain language summary
Otitis externa is a common and often painful condition of the ears of dogs. The probability of otitis externa varies widely between dogs depending on their tendency towards other skin problems such as allergic skin disease. However, breed-related anatomical features such as the degree and point of folding of the ear flap or the overall size of the dog can act to further predispose towards otitis externa. Greater understanding of these predisposing factors could lead to opportunities for breeders to breed away from predisposing features and also help owners and veterinarians to predict which dogs are most at risk of this painful condition.Veterinarians record clinical notes when dogs visit for veterinary care, and these clinical notes can act as a rich source of information on the health of these dogs. This study accessed anonymised clinical records of almost a million dogs in the UK to identify dogs diagnosed with otitis externa. The breed, age, bodyweight and other information available on these dogs were used to explore why certain dog types were predisposed to otitis externa.A random sample of 22,333 dogs was selected for analysis. Of these, 7.30% (over 7 in a hundred) were diagnosed with otitis externa in a single year. There were 16 breeds with higher risk of otitis externa compared with crossbred dogs. Breeds with the highest risk were Basset Hound (× 5.87), Chinese Shar Pei (× 3.44), Labradoodle (× 2.95), Beagle (× 2.54) and Golden Retriever (× 2.23). Four breeds showed reduced risk: Chihuahua (× 0.20), Border Collie (× 0.34), Yorkshire Terrier (× 0.49) and Jack Russell Terrier (× 0.52). Breeds with pendulous ear carriage (× 1.76) and V-shaped drop ear carriage (× 1.84) had higher risk of otitis externa compared with breeds with erect ear carriage.Breed itself and also breed-associated ear carriage conformation are associated with differing probability of otitis externa in dogs. Better understanding about how these factors affect the probability of otitis externa in dogs can help veterinary practitioners to promote cautious and low-harm approaches to preventing otitis externa (e.g., by advocating ear cleaning with a dry paper cloth, judicious use of ear cleaners with antimicrobial properties and avoidance of overzealous ear-cleaning) and can also assist breeders to breed away from features of dogs that predispose to otitis externa.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dog breeds and conformations predisposed to osteosarcoma in the UK: a VetCompass study.Canine Med Genet. 2023 Jun 27;10(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s40575-023-00131-2. Canine Med Genet. 2023. PMID: 37365662 Free PMC article.
-
Is it now time to iron out the wrinkles? Health of Shar Pei dogs under primary veterinary care in the UK.Canine Med Genet. 2023 Dec 14;10(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s40575-023-00134-z. Canine Med Genet. 2023. PMID: 38093396 Free PMC article.
-
Dog breeds and conformations in the UK in 2019: VetCompass canine demography and some consequent welfare implications.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 26;18(7):e0288081. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288081. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37494312 Free PMC article.
-
A review of techniques for the investigation of otitis externa and otitis media.Clin Tech Small Anim Pract. 2001 Nov;16(4):236-41. doi: 10.1053/svms.2001.27601. Clin Tech Small Anim Pract. 2001. PMID: 11793879 Review.
-
Management of otitis externa.Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1994 Sep;24(5):921-52. doi: 10.1016/s0195-5616(94)50109-8. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1994. PMID: 7817494 Review.
Cited by
-
English Bulldogs in the UK: a VetCompass study of their disorder predispositions and protections.Canine Med Genet. 2022 Jun 15;9(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40575-022-00118-5. Canine Med Genet. 2022. PMID: 35701824 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial resistance and genotyping of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from the ear canals of dogs in Japan.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Jul 20;10:1074127. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1074127. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37546340 Free PMC article.
-
Early life programming by diet can play a role in risk reduction of otitis in dogs.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Nov 6;10:1186131. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1186131. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 38026629 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic visualization and irrigation are essential in management of the recalcitrant discharging canine ear.Can Vet J. 2022 Jul;63(7):755-758. Can Vet J. 2022. PMID: 35784777 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Prevalence of ear disease in cats undergoing cone beam computed tomography for dental procedures.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Mar 14;12:1553585. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1553585. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40191083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carlotti D, Taillieu-Le RS. L’otite externe chez le chien: etiologie et clinique, revue bibliographique et etude retrospective portant sur 752 cas. Pratique Médicale et Chirurgicale de l’Animal de Compagnie. 1997;32:243–257.
-
- Miller W, Griffin C, Campbell K, Muller G. Muller and Kirk’s small animal Dermatology. 7. St. Louis: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2013.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources