Structural proof of a [C-F-C]+ fluoronium cation
- PMID: 34489464
- PMCID: PMC8421340
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-25592-6
Structural proof of a [C-F-C]+ fluoronium cation
Abstract
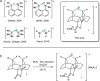
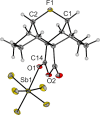
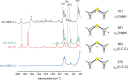
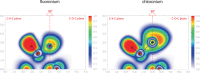
Organic fluoronium ions can be described as positively charged molecules in which the most electronegative and least polarizable element fluorine engages in two partially covalent bonding interactions to two carbon centers. While recent solvolysis experiments and NMR spectroscopic studies on a metastable [C-F-C]+ fluoronium ion strongly support the divalent fluoronium structure over the alternative rapidly equilibrating classical carbocation, the model system has, to date, eluded crystallographic analysis to confirm this phenomenon in the solid state. Herein, we report the single crystal structure of a symmetrical [C-F-C]+ fluoronium cation. Besides its synthesis and crystallographic characterization as the [Sb2F11]- salt, vibrational spectra are discussed and a detailed analysis concerning the nature of the bonding situation in this fluoronium ion and its heavier halonium homologues is performed, which provides detailed insights on this molecular structure.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- McNaught, A. D. & Wilkinson, A. IUPAC. Compendium of Chemical Terminology (the “Gold Book) 2nd edn (Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, 1997).
-
- Roberts I, Kimball GE. The halogenation of ethylenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1937;59:947–948. doi: 10.1021/ja01284a507. - DOI
-
- Grushin VV. Cyclic diaryliodonium ions: old mysteries solved and new applications envisaged. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2000;29:315–324. doi: 10.1039/a909041j. - DOI
-
- Brown RS, et al. Stable bromonium and iodonium ions of the hindered olefins adamantylideneadamantane and bicyclo[3.3.1]nonylidenebicyclo[3.3.1]nonane. X-ray structure, transfer of positive halogens to acceptor olefins, and ab initio studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994;116:2448–2456. doi: 10.1021/ja00085a027. - DOI

