Endothelium-specific depletion of LRP1 improves glucose homeostasis through inducing osteocalcin
- PMID: 34489478
- PMCID: PMC8421392
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-25673-6
Endothelium-specific depletion of LRP1 improves glucose homeostasis through inducing osteocalcin
Abstract
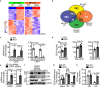
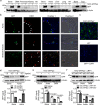
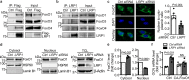
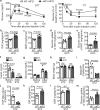
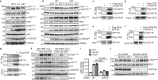
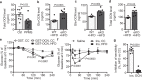
The vascular endothelium is present within metabolic organs and actively regulates energy metabolism. Here we show osteocalcin, recognized as a bone-secreted metabolic hormone, is expressed in mouse primary endothelial cells isolated from heart, lung and liver. In human osteocalcin promoter-driven green fluorescent protein transgenic mice, green fluorescent protein signals are enriched in endothelial cells lining aorta, small vessels and capillaries and abundant in aorta, skeletal muscle and eye of adult mice. The depletion of lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 induces osteocalcin through a Forkhead box O -dependent pathway in endothelial cells. Whereas depletion of osteocalcin abolishes the glucose-lowering effect of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 depletion, osteocalcin treatment normalizes hyperglycemia in multiple mouse models. Mechanistically, osteocalcin receptor-G protein-coupled receptor family C group 6 member A and insulin-like-growth-factor-1 receptor are in the same complex with osteocalcin and required for osteocalcin-promoted insulin signaling pathway. Therefore, our results reveal an endocrine/paracrine role of endothelial cells in regulating insulin sensitivity, which may have therapeutic implications in treating diabetes and insulin resistance through manipulating vascular endothelium.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Saltiel AR, Kahn CR. Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature. 2001;414:799–806. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL098839/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL061656/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK121348/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL122736/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES027725/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK111436/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK123186/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK114356/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES027544/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA215591/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES030285/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG006348/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL153320/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL112890/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

