Harnessing the CRISPR-Cas Systems to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance
- PMID: 34489905
- PMCID: PMC8418092
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.716064
Harnessing the CRISPR-Cas Systems to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance
Abstract
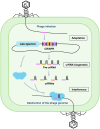
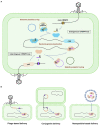
The emergence of antimicrobial-resistant (AMR) bacteria has become one of the most serious threats to global health, necessitating the development of novel antimicrobial strategies. CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)-Cas (CRISPR-associated) system, known as a bacterial adaptive immune system, can be repurposed to selectively target and destruct bacterial genomes other than invasive genetic elements. Thus, the CRISPR-Cas system offers an attractive option for the development of the next-generation antimicrobials to combat infectious diseases especially those caused by AMR pathogens. However, the application of CRISPR-Cas antimicrobials remains at a very preliminary stage and numerous obstacles await to be solved. In this mini-review, we summarize the development of using type I, type II, and type VI CRISPR-Cas antimicrobials to eradicate AMR pathogens and plasmids in the past a few years. We also discuss the most common challenges in applying CRISPR-Cas antimicrobials and potential solutions to overcome them.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas system; antimicrobial resistance; genome targeting; phage delivery; plasmid curing.
Copyright © 2021 Duan, Cao, Zhang and Xu.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

