Different Profiles of Antibodies and Cytokines Were Found Between Severe and Moderate COVID-19 Patients
- PMID: 34489974
- PMCID: PMC8417126
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.723585
Different Profiles of Antibodies and Cytokines Were Found Between Severe and Moderate COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
Objectives: Our objective was to determine the antibody and cytokine profiles in different COVID-19 patients.
Methods: COVID-19 patients with different clinical classifications were enrolled in this study. The level of IgG antibodies, IgA, IgM, IgE, and IgG subclasses targeting N and S proteins were tested using ELISA. Neutralizing antibody titers were determined by using a toxin neutralization assay (TNA) with live SARS-CoV-2. The concentrations of 8 cytokines, including IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, CCL2, CXCL10, IFN-γ, and TNF-α, were measured using the Protein Sample Ella-Simple ELISA system. The differences in antibodies and cytokines between severe and moderate patients were compared by t-tests or Mann-Whitney tests.
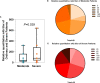
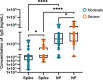
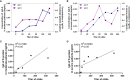
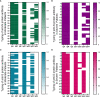
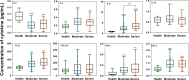
Results: A total of 79 COVID-19 patients, including 49 moderate patients and 30 severe patients, were enrolled. Compared with those in moderate patients, neutralizing antibody and IgG-S antibody titers in severe patients were significantly higher. The concentration of IgG-N antibody was significantly higher than that of IgG-S antibody in COVID-19 patients. There was a significant difference in the distribution of IgG subclass antibodies between moderate patients and severe patients. The positive ratio of anti-S protein IgG3 is significantly more than anti-N protein IgG3, while the anti-S protein IgG4 positive rate is significantly less than the anti-N protein IgG4 positive rate. IL-2 was lower in COVID-19 patients than in healthy individuals, while IL-4, IL-6, CCL2, IFN-γ, and TNF-α were higher in COVID-19 patients than in healthy individuals. IL-6 was significantly higher in severe patients than in moderate patients. The antibody level of anti-S protein was positively correlated with the titer of neutralizing antibody, but there was no relationship between cytokines and neutralizing antibody.
Conclusions: Our findings show the severe COVID-19 patients' antibody levels were stronger than those of moderate patients, and a cytokine storm is associated with COVID-19 severity. There was a difference in immunoglobulin type between anti-S protein antibodies and anti-N protein antibodies in COVID-19 patients. And clarified the value of the profile in critical prevention.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; cytokine; immunoglobulin type; neutralizing antibody.
Copyright © 2021 Guo, Li, Xia, Su, Li, Feng, Han, Wang, Jia, Bao, Li, Liu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

