Overexpression of MsRCI2A, MsRCI2B, and MsRCI2C in Alfalfa (Medicago sativ a L.) Provides Different Extents of Enhanced Alkali and Salt Tolerance Due to Functional Specialization of MsRCI2s
- PMID: 34490005
- PMCID: PMC8417119
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.702195
Overexpression of MsRCI2A, MsRCI2B, and MsRCI2C in Alfalfa (Medicago sativ a L.) Provides Different Extents of Enhanced Alkali and Salt Tolerance Due to Functional Specialization of MsRCI2s
Abstract
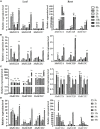
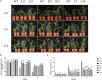
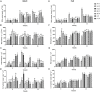
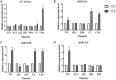
Rare cold-inducible 2/plasma membrane protein 3 (RCI2/PMP3) genes are ubiquitous in plants and belong to a multigene family whose members respond to a variety of abiotic stresses by regulating ion homeostasis and stabilizing membranes, thus preventing damage. In this study, the expression of MsRCI2A, MsRCI2B, and MsRCI2C under high-salinity, alkali and ABA treatments was analyzed. The results showed that the expression of MsRCI2A, MsRCI2B, and MsRCI2C in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) was induced by salt, alkali and ABA treatments, but there were differences between MsRCI2 gene expression under different treatments. We investigated the functional differences in the MsRCI2A, MsRCI2B, and MsRCI2C proteins in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) by generating transgenic alfalfa plants that ectopically expressed these MsRCI2s under the control of the CaMV35S promoter. The MsRCI2A/B/C-overexpressing plants exhibited different degrees of improved phenotypes under high-salinity stress (200 mmol.L-1 NaCl) and weak alkali stress (100 mmol.L-1 NaHCO3, pH 8.5). Salinity stress had a more significant impact on alfalfa than alkali stress. Overexpression of MsRCI2s in alfalfa caused the same physiological response to salt stress. However, in response to alkali stress, the three proteins encoded by MsRCI2s exhibited functional differences, which were determined not only by their different expression regulation but also by the differences in their regulatory relationship with MsRCI2s or H+-ATPase.
Keywords: Medicago saliva L.; RCI2 genes; alkali tolerance; gene overexpression; salt tolerance.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Song, Zhan, Cong, Xu, Dong and Cai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Overexpression of MsRCI2D and MsRCI2E Enhances Salt Tolerance in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) by Stabilizing Antioxidant Activity and Regulating Ion Homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 29;23(17):9810. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179810. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077224 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of the MsRCI2 Gene Family in Medicago sativa and Functional Characterization of MsRCI2B in Salt Tolerance.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 27;26(9):4165. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094165. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362404 Free PMC article.
-
The synergistic roles of MsRCI2B and MsRCI2E in the regulation of ion balance and ROS homeostasis in alfalfa under salt stress.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Apr;300:140093. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140093. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 39863229
-
Isolation and functional characterization of salt-stress induced RCI2-like genes from Medicago sativa and Medicago truncatula.J Plant Res. 2015 Jul;128(4):697-707. doi: 10.1007/s10265-015-0715-x. Epub 2015 Mar 24. J Plant Res. 2015. PMID: 25801273
-
Plant abiotic stress-related RCI2/PMP3s: multigenes for multiple roles.Planta. 2016 Jan;243(1):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s00425-015-2386-1. Epub 2015 Aug 26. Planta. 2016. PMID: 26306604 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Physiological and Transcriptome Profiles Uncover Salt Tolerance Mechanisms in Alfalfa.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jun 9;13:931619. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.931619. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35755671 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium channels and transporters: Roles in response to biotic and abiotic stresses.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Sep 8;13:964059. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.964059. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36161014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Forage Crop Research in the Modern Age.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jul;12(27):e2415631. doi: 10.1002/advs.202415631. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40586694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding of Plant Salt Tolerance Mechanisms and Application to Molecular Breeding.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 11;25(20):10940. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010940. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of MsRCI2D and MsRCI2E Enhances Salt Tolerance in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) by Stabilizing Antioxidant Activity and Regulating Ion Homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 29;23(17):9810. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179810. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077224 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ben R. W., Ben S. R., Meynard D., Verdeil J. L., Azaza J., Zouari N., et al. (2017). Ectopic expression of Aeluropus littoralis plasma membrane protein gene AlTMP1 confers abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco by improving water status and cation homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18:692. 10.3390/ijms18040692 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ben R. W., Ben S. R., Meynard D., Zouari N., Mahjoub A., Fki L., et al. (2018). Overexpression of AlTMP2 gene from the halophyte grass Aeluropus littoralis in transgenic tobacco enhances tolerance to different abiotic stresses by improving membrane stability and deregulating some stress-related genes. Protoplasma 255 1161–1177. 10.1007/s00709-018-1223-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dong X., Im S. B., Lim Y. P., Nou I. S., Hur Y. (2014). Comparative transcriptome profiling of freezing stress responsiveness in two contrasting Chinese cabbage genotypes, Chiifu and Kenshin. Genes Genomics 36 215–227. 10.1007/s13258-013-0160-y - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

