Predicting LncRNA-Disease Association by a Random Walk With Restart on Multiplex and Heterogeneous Networks
- PMID: 34490041
- PMCID: PMC8417042
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.712170
Predicting LncRNA-Disease Association by a Random Walk With Restart on Multiplex and Heterogeneous Networks
Abstract
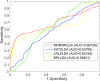
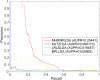
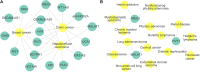
Studies have found that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play important roles in many human biological processes, and it is critical to explore potential lncRNA-disease associations, especially cancer-associated lncRNAs. However, traditional biological experiments are costly and time-consuming, so it is of great significance to develop effective computational models. We developed a random walk algorithm with restart on multiplex and heterogeneous networks of lncRNAs and diseases to predict lncRNA-disease associations (MHRWRLDA). First, multiple disease similarity networks are constructed by using different approaches to calculate similarity scores between diseases, and multiple lncRNA similarity networks are also constructed by using different approaches to calculate similarity scores between lncRNAs. Then, a multiplex and heterogeneous network was constructed by integrating multiple disease similarity networks and multiple lncRNA similarity networks with the lncRNA-disease associations, and a random walk with restart on the multiplex and heterogeneous network was performed to predict lncRNA-disease associations. The results of Leave-One-Out cross-validation (LOOCV) showed that the value of Area under the curve (AUC) was 0.68736, which was improved compared with the classical algorithm in recent years. Finally, we confirmed a few novel predicted lncRNAs associated with specific diseases like colon cancer by literature mining. In summary, MHRWRLDA contributes to predict lncRNA-disease associations.
Keywords: association; disease; lncRNA; networks; predict; random walk.
Copyright © 2021 Yao, Ji, Lv, Li, Xiang, Liao and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
BJ was employed by Geneis Beijing Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handling editor declared a past co-authorship with one of the authors JX.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

