Development of humoral and cellular immunological memory against SARS-CoV-2 despite B cell depleting treatment in multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 34490414
- PMCID: PMC8410640
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103078
Development of humoral and cellular immunological memory against SARS-CoV-2 despite B cell depleting treatment in multiple sclerosis
Abstract
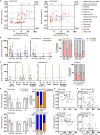
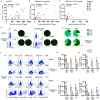
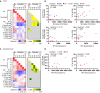
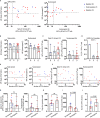
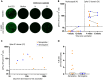
B cell depleting therapies (BCDTs) are widely used as immunomodulating agents for autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis. Their possible impact on development of immunity to severe acute respiratory syndrome virus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) has raised concerns with the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. We here evaluated the frequency of COVID-19-like symptoms and determined immunological responses in participants of an observational trial comprising several multiple sclerosis disease modulatory drugs (COMBAT-MS; NCT03193866) and in eleven patients after vaccination, with a focus on BCDT. Almost all seropositive and 17.9% of seronegative patients on BCDT, enriched for a history of COVID-19-like symptoms, developed anti-SARS-CoV-2 T cell memory, and T cells displayed functional similarity to controls producing IFN-γ and TNF. Following vaccination, vaccine-specific humoral memory was impaired, while all patients developed a specific T cell response. These results indicate that BCDTs do not abrogate SARS-CoV-2 cellular memory and provide a possible explanation as to why the majority of patients on BCDTs recover from COVID-19.
Keywords: Immunology; Virology.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
T.O. has received unrestricted grants for extended multiple sclerosis studies in relation to COVID-19 from Biogen and Merck. Not related to this manuscript, T.O. has received unrestricted grants, advisory board/ lectures from Biogen, Merck, Novartis, and Sanofi, and F.P. has received research grants from Genzyme, Merck KGaA, and UCB and fees for serving as Chair of DMC in clinical trials with Parexel. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multiple Sclerosis and SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination: Considerations for Immune-Depleting Therapies.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Jan 28;9(2):99. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9020099. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33525459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 infection in immunocompromised patients: humoral versus cell-mediated immunity.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Jul;8(2):e000862. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000862. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32727811 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary evidence of blunted humoral response to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in multiple sclerosis patients treated with ocrelizumab.Neurol Sci. 2021 Sep;42(9):3523-3526. doi: 10.1007/s10072-021-05397-7. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Neurol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34128150 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 antibody responses following Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination in a patient with multiple sclerosis treated with ocrelizumab: a case report.J Int Med Res. 2021 Sep;49(9):3000605211044378. doi: 10.1177/03000605211044378. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34528472 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 antibody dynamics and B-cell memory response over time in COVID-19 convalescent subjects.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021 Sep;27(9):1349.e1-1349.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.008. Epub 2021 May 8. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021. PMID: 33975009 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clonal diversity predicts persistence of SARS-CoV-2 epitope-specific T-cell response.Commun Biol. 2022 Dec 9;5(1):1351. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-04250-7. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36494499 Free PMC article.
-
Immunocompetence after SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Patient with Multiple Sclerosis Treated with Ofatumumab: A Case Report.Case Rep Neurol. 2022 Aug 16;14(2):320-325. doi: 10.1159/000524946. eCollection 2022 May-Aug. Case Rep Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36160655 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid and vaccine-induced immunity against SAR-CoV-2 in MS patients on different disease-modifying therapies.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2022 Oct;9(10):1643-1659. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51664. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36165097 Free PMC article.
-
Strong T-cell activation in response to COVID-19 vaccination in multiple sclerosis patients receiving B-cell depleting therapies.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 5;13:926318. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.926318. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35990701 Free PMC article.
-
Rituximab-treated patients with lymphoma develop strong CD8 T-cell responses following COVID-19 vaccination.Br J Haematol. 2022 Jun;197(6):697-708. doi: 10.1111/bjh.18149. Epub 2022 Mar 21. Br J Haematol. 2022. PMID: 35254660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achiron A., Mandel M., Dreyer-Alster S., Harari G., Magalashvili D., Sonis P., Dolev M., Menascu S., Flechter S., Falb R., Gurevich M. Humoral immune response to COVID-19 mRNA vaccine in patients with multiple sclerosis treated with high-efficacy disease-modifying therapies. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2021;14 doi: 10.1177/17562864211012835. 17562864211012835. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bar-Or A., Calkwood J.C., Chognot C., Evershed J., Fox E.J., Herman A., Manfrini M., McNamara J., Robertson D.S., Stokmaier D. Effect of ocrelizumab on vaccine responses in patients with multiple sclerosis: the VELOCE study. Neurology. 2020;95:e1999–e2008. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000010380. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

