Remote ischemic post‑conditioning alleviates ischemia/reperfusion‑induced intestinal injury via the ERK signaling pathway‑mediated RAGE/HMGB axis
- PMID: 34490475
- PMCID: PMC8441982
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12413
Remote ischemic post‑conditioning alleviates ischemia/reperfusion‑induced intestinal injury via the ERK signaling pathway‑mediated RAGE/HMGB axis
Abstract
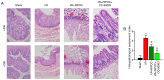
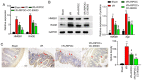
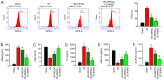
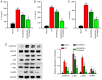
Intestinal ischemia reperfusion (I/R) injury is a tissue and organ injury that frequently occurs during surgery and significantly contributes to the pathological processes of severe infection, injury, shock, cardiopulmonary insufficiency and other diseases. However, the mechanism of intestinal I/R injury remains to be elucidated. A mouse model of intestinal I/R injury was successfully established and the model mice were treated with remote ischemic post‑conditioning (RIPOC) and/or an ERK inhibitor (CC‑90003), respectively. Histopathological changes of the intestinal mucosa were determined by hematoxylin and eosin staining. In addition, the levels of high‑mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) and receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) expression were confirmed by reverse transcription‑quantitative polymerase chain reaction, western blotting and immunohistochemistry assays. The levels of antioxidants, oxidative stress markers (8‑OHdG) and interleukin 1 family members were evaluated by ELISA assays and the levels of NF‑κB pathway proteins were analyzed by western blotting. The data demonstrated that RIPOC could attenuate the histopathological features of intestinal mucosa in the intestinal I/R‑injury mouse models via the ERK pathway. It was also revealed that HMGB1 and RAGE expression in the mouse models could be markedly reduced by RIPOC (P<0.05) and that these reductions were associated with inhibition of the ERK pathway. Furthermore, it was demonstrated that RIPOC produced significant antioxidant and anti‑inflammatory effects following an intestinal I/R injury and that these effects were mediated via the ERK pathway (P<0.05). In addition, RIPOC was demonstrated to suppress the NF‑κB (p65)/NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammatory pathways in the intestinal I/R injury mouse models via the ERK pathway. The findings of the present study demonstrated that RIPOC helped to protect mice with an intestinal I/R injury by downregulating the ERK pathway.
Keywords: antioxidants; extracellular signal‑regulated kinase; inflammation; ischemia‑reperfusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

