Influence of surface topography on PCL electrospun scaffolds for liver tissue engineering
- PMID: 34491259
- PMCID: PMC8493469
- DOI: 10.1039/d1tb00789k
Influence of surface topography on PCL electrospun scaffolds for liver tissue engineering
Abstract
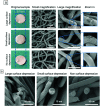
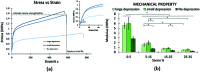
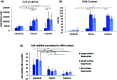
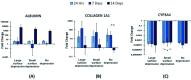
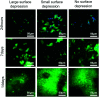
Severe liver disease is one of the most common causes of death globally. Currently, whole organ transplantation is the only therapeutic method for end-stage liver disease treatment, however, the need for donor organs far outweighs demand. Recently liver tissue engineering is starting to show promise for alleviating part of this problem. Electrospinning is a well-known method to fabricate a nanofibre scaffold which mimics the natural extracellular matrix that can support cell growth. This study aims to investigate liver cell responses to topographical features on electrospun fibres. Scaffolds with large surface depression (2 μm) (LSD), small surface depression (0.37 μm) (SSD), and no surface depression (NSD) were fabricated by using a solvent-nonsolvent system. A liver cell line (HepG2) was seeded onto the scaffolds for up to 14 days. The SSD group exhibited higher levels of cell viability and DNA content compared to the other groups. Additionally, the scaffolds promoted gene expression of albumin, with all cases having similar levels, while the cell growth rate was altered. Furthermore, the scaffold with depressions showed 0.8 MPa higher ultimate tensile strength compared to the other groups. These results suggest that small depressions might be preferred by HepG2 cells over smooth and large depression fibres and highlight the potential for tailoring liver cell responses.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

References
-
- British Liver Trust, The alarming impact of liver disease in the UK, Bournemouth, 2019
-
- Williams R. Alexander G. Armstrong I. Baker A. Bhala N. Camps-walsh G. Cramp M. E. De Lusignan S. Day N. Dhawan A. Dillon J. Drummond C. Dyson J. Foster G. Gimore I. Hudson M. Kelly D. Langford A. McDougall N. Meier P. Moriarty K. Newsome P. O’Grady J. Pryke R. Rolfe L. Rice P. Rutter H. Sheron N. Taylor A. Thompson J. Thorburn D. Verne J. Wass J. Yeoman A. Disease burden and costs from excess alcohol consumption, obesity, and viral hepatitis: fourth report of the Lancet Standing Commission on Liver Disease in the UK. Lancet. 2018;391(10125):1097–1107. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32866-0. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32866-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Grant R. Hay D. Callanan A. From scaffold to structure: the synthetic production of cell derived extracellular matrix for liver tissue engineering From scaffold to structure: the synthetic production of cell derived extracellular matrix for liver tissue engineering. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express. 2018;4(6):65015. doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/aacbe1. doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/aacbe1. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

