Multiplatform Assessment of Saliva for SARS-CoV-2 Molecular Detection in Symptomatic Healthcare Personnel and Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department
- PMID: 34491341
- PMCID: PMC8499908
- DOI: 10.1093/jalm/jfab115
Multiplatform Assessment of Saliva for SARS-CoV-2 Molecular Detection in Symptomatic Healthcare Personnel and Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department
Abstract
Background: Saliva has garnered great interest as an alternative specimen type for molecular detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Data are limited on the relative performance of different molecular methods using saliva specimens and the relative sensitivity of saliva to nasopharyngeal (NP) swabs.
Methods: To address the gap in knowledge, we enrolled symptomatic healthcare personnel (n = 250) from Barnes-Jewish Hospital/Washington University Medical Center and patients presenting to the Emergency Department with clinical symptoms compatible with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19; n = 292). We collected paired saliva specimens and NP swabs. The Lyra SARS-CoV-2 assay (Quidel) was evaluated on paired saliva and NP samples. Subsequently we compared the Simplexa COVID-19 Direct Kit (Diasorin) and a modified SalivaDirect (Yale) assay on a subset of positive and negative saliva specimens.
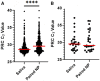
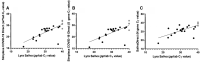
Results: The positive percent agreement (PPA) between saliva and NP samples using the Lyra SARS-CoV-2 assay was 63.2%. Saliva samples had higher SARS-CoV-2 cycle threshold values compared to NP swabs (P < 0.0001). We found a 76.47% (26/34) PPA for Simplexa COVID-19 Direct Kit on saliva and a 67.6% (23/34) PPA for SalivaDirect compared to NP swab results.
Conclusion: These data demonstrate molecular assays have variability in performance for detection of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva.
© American Association for Clinical Chemistry 2021. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 PCR-Based Detection Using Saliva or Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimens in Asymptomatic Populations.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Sep 3;9(1):e0006221. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00062-21. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34431689 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Performance of Self-Collected Saliva Versus Nasopharyngeal Swab for the Molecular Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in the Clinical Setting.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0046821. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00468-21. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34730436 Free PMC article.
-
Saliva is Comparable to Nasopharyngeal Swabs for Molecular Detection of SARS-CoV-2.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Sep 3;9(1):e0016221. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00162-21. Epub 2021 Aug 18. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34406838 Free PMC article.
-
Variation in SARS-CoV-2 molecular test sensitivity by specimen types in a large sample of emergency department patients.Am J Emerg Med. 2021 Dec;50:381-387. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2021.08.034. Epub 2021 Aug 17. Am J Emerg Med. 2021. PMID: 34478943 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative clinical specimens for the detection of SARS-CoV-2: A rapid review.Rev Med Virol. 2021 Jul;31(4):e2185. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2185. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Rev Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 33091200 Review.
Cited by
-
Saliva as a diagnostic specimen for SARS-CoV-2 detection: A scoping review.Oral Dis. 2022 Nov;28 Suppl 2:2362-2390. doi: 10.1111/odi.14216. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Oral Dis. 2022. PMID: 35445491 Free PMC article.
-
Salivary SARS-CoV-2 RNA for diagnosis of COVID-19 patients: a systematic revisew and meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy.Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2023 Jun 21;59:219-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jdsr.2023.06.004. Online ahead of print. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2023. PMID: 37360001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Laboratory-based molecular test alternatives to RT-PCR for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 14;10(10):CD015618. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015618. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39400904
-
The effect of sample site and collection procedure on identification of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 16;12(12):CD014780. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014780. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39679851 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bilder L, Machtei EE, Shenhar Y, Kra-Oz Z, Basis F. Salivary detection of H1N1 virus: a clinical feasibility investigation. J Dent Res 2011;90:1136–9. - PubMed
-
- Sueki A, Matsuda K, Yamaguchi A, Uehara M, Sugano M, Uehara T, Honda T. Evaluation of saliva as diagnostic materials for influenza virus infection by PCR-based assays. Clin Chim Acta 2016;453:71–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

