Axillary ultrasonography combined with pre-operative wire localisation of clipped node in nodal restaging after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in node positive breast cancer patients: a pilot study
- PMID: 34491822
- PMCID: PMC8553197
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20210788
Axillary ultrasonography combined with pre-operative wire localisation of clipped node in nodal restaging after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in node positive breast cancer patients: a pilot study
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the role of axillary ultrasonography (axUS) and ultrasound-guided pre-operative wire localisation of pre-treatment positive clipped node (CN) for prediction of nodal response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) in node positive breast carcinoma patients.
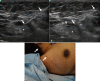
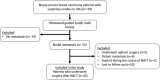
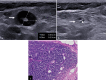
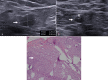
Methods and materials: A prospective study was conducted between June 2018 and August 2020 after Ethics Committee approval. Breast carcinoma patients (cT1-cT4b) with palpable axillary nodes (cN1-cN3) and suitable for NACT were recruited after written informed consent. Single, most suspicious node was biopsied and clipped. Nodal response to NACT was assessed on axUS. Wire localisation of CN was performed prior to axillary lymph node dissection (ALND). Diagnostic performances of axUS and CN excision were assessed.
Results: Of the 69 patients evaluated, 32 patients (mean age, 43.5 ± 11.8 years; females, 31/32 [97%]; pre-menopausal, 18/32 [56.3%]) with metastatic nodes who received NACT were included. Nodal pathological complete response rate was 34.4% (11/32) overall and 70% (7/10) in patients with ≤2 suspicious nodes on pre-NACT axUS. False-negative rates (FNRs) of axUS and CN excision were 4.8% and 28.6% respectively. Combination of post-NACT axUS and CN excision had an FNR of 4.8% overall and 0% in patients with ≤2 suspicious nodes on pre-NACT axUS.
Conclusion: Combination of AxUS and ultrasound-guided wire localisation of pre-treatment positive CN has high diagnostic accuracy for nodal restaging after NACT in node positive breast cancer patients.
Advances in knowledge: Addition of axUS assessment to wire localisation of CN reduces its FNR for detecting residual metastasis after NACT.
Figures
References
-
- Nice.org.uk. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Web site. Early and locally advanced breast cancer: diagnosis and management NICE guideline [NG101]. Available from: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng101 [Accessed 18 July 2018]. - PubMed
-
- Rebegea L, Firescu D, Dumitru M, Anghel R. The incidence and risk factors for occurrence of arm lymphedema after treatment of breast cancer. Chirurgia 2015; 110: 33–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

