Treatment Options for COVID-19-Related Guillain-Barré Syndrome: A Systematic Review of Literature
- PMID: 34491938
- PMCID: PMC8423032
- DOI: 10.1097/NRL.0000000000000342
Treatment Options for COVID-19-Related Guillain-Barré Syndrome: A Systematic Review of Literature
Abstract
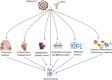
Background: Central nervous system complications are reported in an increasing number of patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). COVID-19-related Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is of particular importance given its association with higher mortality rates and prolonged respiratory failure.
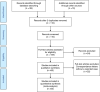
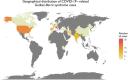
Review summary: We conducted a systematic review of published cases for COVID-19-related GBS, and provide a summary of clinical management strategies for these cases. Sixty-three studies, including 86 patients, were included. Seventy-six cases with reported outcome data were eligible for the outcome analysis. Ninety-nine percent of patients were diagnosed with COVID-19 before diagnosis of GBS (median: 14 d prior, interquartile range: 7 to 20). Intravenous immunotherapy (intravenous immunoglobulin: 0.4 g/kg/d for 5 d) was the most frequently used treatment approach. The review indicated that the outcome was not favorable in 26% of cases (persistent neurological deficits). A mortality rate of 3.5% was observed in patients with COVID-19-related GBS.
Conclusions: Although evidence to support specific treatments is lacking, clinicians should consider the benefits of immunotherapy and plasma exchange in addition to the standard antimicrobial and supportive therapies for patients who meet the diagnostic criteria for acute sensory and motor polyradiculoneuritis. Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment alone is not shown to result in improved outcomes or mortality. More extensive studies aimed at exploring the neurological manifestations and complications of COVID-19 and distinctive treatment options for COVID-19-related GBS are warranted.
Copyright © 2021 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

