Discovery of photosynthesis genes through whole-genome sequencing of acetate-requiring mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
- PMID: 34492001
- PMCID: PMC8448359
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009725
Discovery of photosynthesis genes through whole-genome sequencing of acetate-requiring mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Abstract
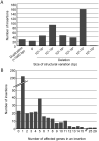
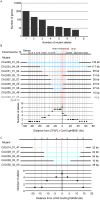
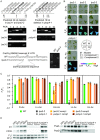
Large-scale mutant libraries have been indispensable for genetic studies, and the development of next-generation genome sequencing technologies has greatly advanced efforts to analyze mutants. In this work, we sequenced the genomes of 660 Chlamydomonas reinhardtii acetate-requiring mutants, part of a larger photosynthesis mutant collection previously generated by insertional mutagenesis with a linearized plasmid. We identified 554 insertion events from 509 mutants by mapping the plasmid insertion sites through paired-end sequences, in which one end aligned to the plasmid and the other to a chromosomal location. Nearly all (96%) of the events were associated with deletions, duplications, or more complex rearrangements of genomic DNA at the sites of plasmid insertion, and together with deletions that were unassociated with a plasmid insertion, 1470 genes were identified to be affected. Functional annotations of these genes were enriched in those related to photosynthesis, signaling, and tetrapyrrole synthesis as would be expected from a library enriched for photosynthesis mutants. Systematic manual analysis of the disrupted genes for each mutant generated a list of 253 higher-confidence candidate photosynthesis genes, and we experimentally validated two genes that are essential for photoautotrophic growth, CrLPA3 and CrPSBP4. The inventory of candidate genes includes 53 genes from a phylogenomically defined set of conserved genes in green algae and plants. Altogether, 70 candidate genes encode proteins with previously characterized functions in photosynthesis in Chlamydomonas, land plants, and/or cyanobacteria; 14 genes encode proteins previously shown to have functions unrelated to photosynthesis. Among the remaining 169 uncharacterized genes, 38 genes encode proteins without any functional annotation, signifying that our results connect a function related to photosynthesis to these previously unknown proteins. This mutant library, with genome sequences that reveal the molecular extent of the chromosomal lesions and resulting higher-confidence candidate genes, will aid in advancing gene discovery and protein functional analysis in photosynthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exists.
Figures