Raja 42, a novel gamma lactam compound, is effective against Clostridioides difficile
- PMID: 34492076
- PMCID: PMC8423298
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257143
Raja 42, a novel gamma lactam compound, is effective against Clostridioides difficile
Abstract
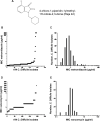
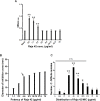
Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) is the primary cause of hospital-acquired diarrhea, and responsible for over 500,000 enteric infections a year in the United States alone. Although most patients with CDI are successfully treated with metronidazole or vancomycin, the high rate of recurrence is still a serious problem, in which case these antibiotics are usually not very effective. The primary objective of this research is to develop a potentially effective therapeutic agent against C. difficile that are resistant to metronidazole or vancomycin. The susceptibility to metronidazole and vancomycin was examined with 194 C. difficile clinical isolates. Sixty of these isolates chosen based on a variety of criteria were examined for their susceptibility against the 4-chloro-1-piperidin-1ylmethyl-1H-indole-2,3-dione compound (Raja 42), a novel isatin-benzothiazole analogue containing a gamma-lactam structure, as we previously found that this novel compound is effective against a variety of different bacteria. Most of the 60 isolates were resistant to ceftriaxone and ciprofloxacin, raising the possibility that they might have been exposed previously to these or structurally similar antibiotics (e.g., β-lactam and quinolone compounds). Among the isolates, 48 (80%) and 54 (90%) were susceptible to metronidazole and vancomycin, respectively. Raja 42 was found to be effective against most of the isolates, especially so against metronidazole-resistant C. difficile. Most importantly, five isolates that show resistance to metronidazole and vancomycin were sensitive to Raja 42. Thus, Raja 42, a gamma lactam antibiotic, has the potential to effectively control C. difficile strains that are resistant to metronidazole and vancomycin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

