Impact of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs on vaccine immunogenicity in patients with inflammatory rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases
- PMID: 34493491
- PMCID: PMC8494475
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221244
Impact of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs on vaccine immunogenicity in patients with inflammatory rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases
Abstract
Patients with rheumatic diseases are at increased risk of infectious complications; vaccinations are a critical component of their care. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs may reduce the immunogenicity of common vaccines. We will review here available data regarding the effect of these medications on influenza, pneumococcal, herpes zoster, SARS-CoV-2, hepatitis B, human papilloma virus and yellow fever vaccines. Rituximab has the most substantial impact on vaccine immunogenicity, which is most profound when vaccinations are given at shorter intervals after rituximab dosing. Methotrexate has less substantial effect but appears to adversely impact most vaccine immunogenicity. Abatacept likely decrease vaccine immunogenicity, although these studies are limited by the lack of adequate control groups. Janus kinase and tumour necrosis factor inhibitors decrease absolute antibody titres for many vaccines, but do not seem to significantly impact the proportions of patients achieving seroprotection. Other biologics (interleukin-6R (IL-6R), IL-12/IL-23 and IL-17 inhibitors) have little observed impact on vaccine immunogenicity. Data regarding the effect of these medications on the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine immunogenicity are just now emerging, and early glimpses appear similar to our experience with other vaccines. In this review, we summarise the most recent data regarding vaccine response and efficacy in this setting, particularly in light of current vaccination recommendations for immunocompromised patients.
Keywords: antirheumatic agents; methotrexate; rituximab; tumour necrosis factor inhibitors; vaccination.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MAF has received consulting fees for Revolo. JTR serves on ACIP HZ Workgroup, lead of ACR COVID Vaccine Guidance Task Force, member of ACR COVID-19 Vaccine Clinical Guideline Task Force, and is a member of EULAR Vaccine Guidance Task Force. JTR receives research grants and/or consulting for unrelated work: Amgen, Abbvie, BMS, CORRONA, Genentech, GSK, Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB. KLW receives support from BMS and Pfizer. KLW has received consulting fees from Pfizer, AbbVie, Union Chimique Belge (UCB), Eli Lilly & Company, Galapagos, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Roche, Gilead, BMS, Regeneron, Sanofi, AstraZeneca and Novartis.
Figures
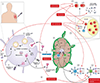
References
-
- Furer V, Rondaan C, Heijstek M, et al. Incidence and prevalence of vaccine preventable infections in adult patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases (AIIRD): a systemic literature review informing the 2019 update of the EULAR recommendations for vaccination in adult patients with AIIRD. RMD Open 2019;5(2):e001041. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2019-001041 [published Online First: 2019/11/02] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

