A Glutamate N-Methyl-d-Aspartate (NMDA) Receptor Subunit 2B-Selective Inhibitor of NMDA Receptor Function with Enhanced Potency at Acidic pH and Oral Bioavailability for Clinical Use
- PMID: 34493631
- PMCID: PMC8626636
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.120.000370
A Glutamate N-Methyl-d-Aspartate (NMDA) Receptor Subunit 2B-Selective Inhibitor of NMDA Receptor Function with Enhanced Potency at Acidic pH and Oral Bioavailability for Clinical Use
Abstract
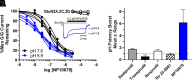
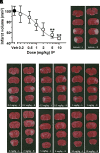
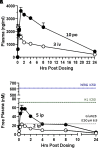
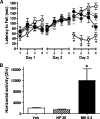
We describe a clinical candidate molecule from a new series of glutamate N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit 2B-selective inhibitors that shows enhanced inhibition at extracellular acidic pH values relative to physiologic pH. This property should render these compounds more effective inhibitors of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors at synapses responding to a high frequency of action potentials, since glutamate-containing vesicles are acidic within their lumen. In addition, acidification of penumbral regions around ischemic tissue should also enhance selective drug action for improved neuroprotection. The aryl piperazine we describe here shows strong neuroprotective actions with minimal side effects in preclinical studies. The clinical candidate molecule NP10679 has high oral bioavailability with good brain penetration and is suitable for both intravenous and oral dosing for therapeutic use in humans. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: This study identifies a new series of glutamate N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor subunit 2B-selective negative allosteric modulators with properties appropriate for clinical advancement. The compounds are more potent at acidic pH, associated with ischemic tissue, and this property should increase the therapeutic safety of this class by improving efficacy in affected tissue while sparing NMDA receptor block in healthy brain.
Copyright © 2021 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Abe TMatsumura SKatano TMabuchi TTakagi KXu LYamamoto AHattori KYagi TWatanabe M, et al. (2005) Fyn kinase-mediated phosphorylation of NMDA receptor NR2B subunit at Tyr1472 is essential for maintenance of neuropathic pain. Eur J Neurosci 22:1445–1454. - PubMed
-
- Addy C, Assaid C, Hreniuk D, Stroh M, Xu Y, Herring WJ, Ellenbogen A, Jinnah HA, Kirby L, Leibowitz MT, et al. (2009) Single-dose administration of MK-0657, an NR2B-selective NMDA antagonist, does not result in clinically meaningful improvement in motor function in patients with moderate Parkinson’s disease. J Clin Pharmacol 49:856–864. - PubMed
-
- Albers GW, Goldstein LB, Hall D, Lesko LM; Aptiganel Acute Stroke Investigators (2001) Aptiganel hydrochloride in acute ischemic stroke: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 286:2673–2682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

