Contrasting Iran's air quality improvement during COVID-19 with other global cities
- PMID: 34493956
- PMCID: PMC8412974
- DOI: 10.1007/s40201-021-00735-5
Contrasting Iran's air quality improvement during COVID-19 with other global cities
Abstract
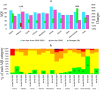
Background and purpose: In late 2019, a novel infectious disease (COVID-19) was identified in Wuhan China, which turned into a global pandemic. Countries all over the world have implemented some sort of lockdown to slow down its infection and mitigate it. This study investigated the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on air quality during 1st January to 30th April 2020 compared to the same period in 2016-2019 in ten Iranian cities and four major cities in the world.
Methods: In this study, the required data were collected from reliable sites. Then, using SPSS and Excel software, the data were analyzed in two intervals before and after the corona pandemic outbreak. The results are provided within tables and charts.
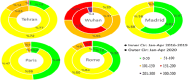
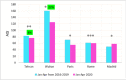
Results: The current study showed the COVID-19 lockdown positively affected Iran's air quality. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the four-month mean air quality index (AQI) values in Tehran, Wuhan, Paris, and Rome were 76, 125, 55, and 60, respectively, which are 8 %, 22 %, 21 %, and 2 % lower than those during the corresponding period (83, 160, 70, and 61) from 2016 to 2019.
Conclusions: Although the outbreak of coronavirus has imposed devastating impacts on economy and health, it can have positive effects on air quality, according to the results.
Keywords: AQI; Air quality; COVID-19; Coronavirus; Lockdown.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no known conflict of interest, competing financial interests, or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Almond D, Du X, Zhang S. Ambiguous pollution response to COVID-19 in China. Cambridge: National Bureau of Economic Research; 2020.
-
- Anjum NA. Good in The Worst: COVID-19 Restrictions and Ease in Global Air Pollution; 2020. 10.20944/preprints202004.0069.v1
-
- Chang H-H, Meyerhoefer C, Yang F-A. COVID-19 prevention and air pollution in the absence of a lockdown. Cambridge: National Bureau of Economic Research; 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

