Modeling the effects of the contaminated environments on COVID-19 transmission in India
- PMID: 34493968
- PMCID: PMC8413511
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104774
Modeling the effects of the contaminated environments on COVID-19 transmission in India
Abstract
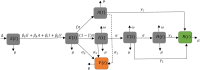
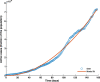
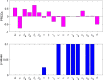
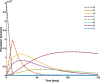
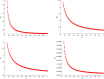
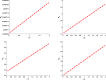
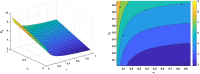
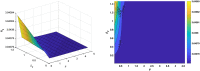
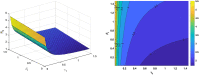
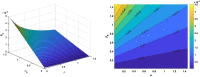
COVID-19 is an infectious disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus that caused an outbreak of typical pneumonia first in Wuhan and then globally. Although researchers focus on the human-to-human transmission of this virus but not much research is done on the dynamics of the virus in the environment and the role humans play by releasing the virus into the environment. In this paper, a novel nonlinear mathematical model of the COVID-19 epidemic is proposed and analyzed under the effects of the environmental virus on the transmission patterns. The model consists of seven population compartments with the inclusion of contaminated environments means there is a chance to get infected by the virus in the environment. We also calculated the threshold quantity to know the disease status and provide conditions that guarantee the local and global asymptotic stability of the equilibria using Volterra-type Lyapunov functions, LaSalle's invariance principle, and the Routh-Hurwitz criterion. Furthermore, the sensitivity analysis is performed for the proposed model that determines the relative importance of the disease transmission parameters. Numerical experiments are performed to illustrate the effectiveness of the obtained theoretical results.
Keywords: 00A71; 34D20; 37M05; 65P40; 92B05; 92Bxx; COVID-19 dynamics; Contaminated environments; Mathematical model; Numerical simulations; Sensitivity analysis; Stability analysis.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Design of a nonlinear model for the propagation of COVID-19 and its efficient nonstandard computational implementation.Appl Math Model. 2021 Jan;89:1835-1846. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2020.08.082. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Appl Math Model. 2021. PMID: 32982020 Free PMC article.
-
Threshold Dynamics of an Epidemic Model with Nonlinear Incidence Rates.Differ Equ Dyn Syst. 2021 Sep 15:1-14. doi: 10.1007/s12591-021-00581-9. Online ahead of print. Differ Equ Dyn Syst. 2021. PMID: 34539106 Free PMC article.
-
How do the contaminated environment influence the transmission dynamics of COVID-19 pandemic?Eur Phys J Spec Top. 2022;231(18-20):3697-3716. doi: 10.1140/epjs/s11734-022-00648-w. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Eur Phys J Spec Top. 2022. PMID: 36033354 Free PMC article.
-
Time-delayed modelling of the COVID-19 dynamics with a convex incidence rate.Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;35:101124. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2022.101124. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022. PMID: 36406926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Universal screening for SARS-CoV-2 infection: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 15;9(9):CD013718. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013718. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33502003 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Stability analysis and numerical evaluations of a COVID-19 model with vaccination.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2024 Apr 27;24(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12874-024-02209-2. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2024. PMID: 38678207 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between COVID-19 Cases and Environmental Contaminants in Quito, Ecuador.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024 Oct 9;21(10):1336. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21101336. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39457309 Free PMC article.
-
A novel fractional order model of SARS-CoV-2 and Cholera disease with real data.J Comput Appl Math. 2023 May 15;423:114969. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2022.114969. Epub 2022 Dec 1. J Comput Appl Math. 2023. PMID: 36471673 Free PMC article.
-
A COVID-19 Infection Model Considering the Factors of Environmental Vectors and Re-Positives and Its Application to Data Fitting in Japan and Italy.Viruses. 2023 May 19;15(5):1201. doi: 10.3390/v15051201. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37243286 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling Global COVID-19 Dissemination Data After the Emergence of Omicron Variant Using Multipronged Approaches.Curr Microbiol. 2022 Aug 10;79(9):286. doi: 10.1007/s00284-022-02985-4. Curr Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35947199 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
