MicroRNA-375: potential cancer suppressor and therapeutic drug
- PMID: 34494089
- PMCID: PMC8458691
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20211494
MicroRNA-375: potential cancer suppressor and therapeutic drug
Abstract
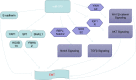
MiR-375 is a conserved noncoding RNA that is known to be involved in tumor cell proliferation, migration, and drug resistance. Previous studies have shown that miR-375 affects the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of human tumor cells via some key transcription factors, such as Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1), Specificity protein 1 (SP1) and signaling pathways (Wnt signaling pathway, nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) pathway and transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) signaling pathway) and is vital for the development of cancer. Additionally, recent studies have identified microRNA (miRNA) delivery system carriers for improved in vivo transportation of miR-375 to specific sites. Here, we discussed the role of miR-375 in different types of cancers, as well as molecular mechanisms, and analyzed the potential of miR-375 as a molecular biomarker and therapeutic target to improve the efficiency of clinical diagnosis of cancer.
Keywords: Dysregulation; EMT; Tumor-suppressive; miR-375.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

