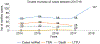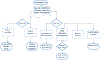Programmatic challenges in managing multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Malawi
- PMID: 34494563
- PMCID: PMC8542254
- DOI: 10.4103/ijmy.ijmy_47_21
Programmatic challenges in managing multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Malawi
Abstract
Background: Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) is one of the most urgent challenges that Malawi tends to take a firm public health action. A recent increase in multidrug MDR-TB cases, a decrease in treatment success rate, and a double increase of lost-to-follow-up call into question the country's programmatic management of MDR-TB (PMDT). As such, the study aimed at exploring programmatic challenges in managing MDR-TB in Malawi.
Methods: A comprehensive and nonsystematic search was made in PubMed and Google Scholar using mainly the keywords "MDR-TB" "extensively drug-resistant TB," Malawi. The study reviewed existing guidelines and gray literature and reviewed data obtained from the national TB program (NTP) as well.
Results: The study found the following challenges affecting PMDT: decrease in funding, partial access to GeneXpert, delay in diagnosis, long treatment duration, lack of adequate personal protective equipment, the long turnaround time of culture results, failure to initiate all diagnosed patients on treatment, absence of alternative second-line medicines, and lack of transport from health facilities to patient homes.
Conclusion: If the Malawi NTP is to achieve a vision of a "TB-free Malawi," rigorous efforts at all levels must be made, including mobilizing domestic resources for improved MDR-TB program performance. Developing partners should continue providing the much-needed funding to the Malawi government to stand in the wake of the MDR-TB crisis.
Keywords: Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis; Malawi; multidrug-resistant tuberculosis; programmatic management.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
References
-
- Kumar A, Singh A, Upadhyay V, Pandey J. Epidemiology of multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis in Northern India. Biomed Biotechnol Res J 2018;2:112.
-
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2020. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020.
-
- World Health Organization. The End TB Strategy. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2012.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous